UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM
For
the fiscal year ended
For the transition period from ___ until ___
Commission
File Number
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s
telephone number, including area code
Securities Registered under Section 12(b) of the Act
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered | ||
| The
|
Securities Registered under Section 12(g) of the Act
Common Stock, par value $.001 per share
Indicate
by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐
Indicate
by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐
Indicate
by check mark whether the issuer (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act
of 1934 during the past 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been
subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule
405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant
was required to submit post such files).
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☐ | Accelerated filer ☐ | |
| Smaller
reporting company | ||
| Emerging
Growth Company |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness
of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered
public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report.
If
securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant
included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements.
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No
The
aggregate market value of the 4,732,068 shares of voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant based on the Nasdaq closing price
on March 31, 2024 was $
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
| Shares Outstanding | ||
| Title of Class | December 19, 2024 | |
| Common Stock |
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| PART I | ||
| Item 1. | Business | 4 |
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 18 |
| Item 1C. | Cybersecurity | 26 |
| Item 2. | Properties | 26 |
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | 26 |
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | 26 |
| PART II | ||
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 27 |
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Conditions and Results of Operations | 27 |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 37 |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | 57 |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | 57 |
| PART III | ||
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 58 |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation | 58 |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners | 58 |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | 58 |
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services | 58 |
| PART IV | ||
| Item 15. | Exhibits | 58 |
| 2 |
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Information
This Annual Report on Form 10-K by Optex Systems Holdings, Inc. (“Optex Systems Holdings,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” or “our”), in particular Part II Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” contains certain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). Any statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. When used in this Annual Report on Form 10- K and other reports, statements, and information we have filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“Commission” or “SEC”), in our press releases, presentations to securities analysts or investors, or in oral statements made by or with the approval of an executive officer, the words or phrases “believes,” “may,” “will,” “expects,” “should,” “continue,” “anticipates,” “intends,” “will likely result,” “estimates,” “projects” or similar expressions and variations thereof are intended to identify such forward-looking statements.
These forward-looking statements represent our expectations, beliefs, intentions or strategies concerning future events, including, but not limited to, any statements regarding our growth strategy; product and development programs; financial performance and financial condition (including revenue, net income, profit margins and working capital); orders and backlog; expected timing of contract deliveries to customers and corresponding revenue recognition; increases in the cost of materials and labor; costs remaining to fulfill contracts; contract loss reserves; labor shortages; follow-on orders; supply chain challenges; the continuation of historical trends; the sufficiency of our cash balances for future liquidity and capital resource needs; the expected impact of changes in accounting policies on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows; anticipated problems and our plans for future operations; and the economy in general or the future of the defense industry.
We caution that these statements by their nature involve risks and uncertainties, certain of which are beyond our control, and actual results may differ materially depending on a variety of important factors. Such risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to, continued funding of defense programs and military spending, the timing of such funding, general economic and business conditions, including unforeseen weakness in the Company’s markets, effects of continued geopolitical unrest and regional conflicts, competition, changes in technology and methods of marketing, delays in completing engineering and manufacturing programs, changes in customer order patterns, changes in product mix, continued success in technological advances and delivering technological innovations, changes in the U.S. Government’s interpretation of federal procurement rules and regulations, changes in spending due to policy changes in any new federal presidential administration, market acceptance of the Company’s products, shortages in components, production delays due to performance quality issues with outsourced components, inability to fully realize the expected benefits from acquisitions and restructurings or delays in realizing such benefits, challenges in integrating acquired businesses and achieving anticipated synergies, changes to export regulations, increases in tax rates, changes to generally accepted accounting principles, difficulties in retaining key employees and customers, unanticipated costs under fixed-price service and system integration engagements, changes in the market for microcap stocks regardless of growth and value and various other factors beyond our control. Some of these risks and uncertainties are identified in this Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and the section “Item 1A Risk Factors” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and you are urged to review that section. You should understand that it is not possible to predict or identify all such factors. Consequently, you should not consider any such list to be a complete list of all potential risks or uncertainties.
We do not assume the obligation to update any forward-looking statement. You should carefully evaluate such statements in light of factors described in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| 3 |
PART I
Item 1. Business
Current Lines of Business
We manufacture optical sighting systems and assemblies for the U.S. Department of Defense, foreign military applications, commercial markets, and consumer markets with the recent acquisition of the Speedtracker Mach product line. Our products are installed on a variety of U.S. military land vehicles, such as the Abrams and Bradley fighting vehicles, light armored and advanced security vehicles and the Stryker family of vehicles. We also manufacture and deliver numerous periscope configurations, rifle and surveillance sights and night vision optical assemblies. Our products consist primarily of build-to-customer print products that are delivered both directly to the armed services and to other defense prime contractors. Less than 1% of our revenue is related to the resale of products substantially manufactured by others. In this case, the product would likely be a simple replacement part of a larger system previously produced by us.
We continue to field new product opportunities from both domestic and international customers. We believe that given continuing unrest in multiple global “hot spots”, the need for precision optics continues to increase. Most of these requirements are for observation and situational awareness applications; however, we continue to see requests for higher magnification and custom reticles in various product modifications. The basic need to protect the soldier while providing information about the mission environment continues to be the primary driver for these requirements.
Recent Events
January 2024 Asset Acquisition
On January 18, 2024, we entered into an asset purchase agreement and a contract manufacturing agreement with RUB Aluminium s.r.o. (“RUB”). Under the agreements, the Company acquired certain intellectual property and technical and marketing information relating to the Speedtracker Mach product line, which is primarily used for firearm projectile speed detection, measuring and tracking. The Company acquired the assets using $1 million cash on hand, with potential additional future cash payments based on successful completion of defined milestones. After the acquisition, the Company determined it would be more economical to move the manufacturing operations in house and is no longer ordering assembled units under the original contract manufacturing agreement. RUB will continue to provide the Company with purchased kit parts for the manufacture of the Speedtracker Mach products.
The acquisition included transaction costs of $30 thousand for legal fees and a contingent liability for payment against an earnout based on meeting certain revenue milestones. As of September 29, 2024, the fair value of the contingent liability was zero. Pursuant to the asset purchase agreement, the total earnout payment will be $238 thousand only if the earnout revenue milestone is achieved during the earnout period, otherwise the earnout will be zero. As of September 29, 2024, the Company determined the likelihood of achieving the revenue milestone during the earnout period was highly unlikely. The intangible asset will be amortized on a straight-line basis over a seven-year period.
Recent Orders
| ● | On December 11, 2024, the Company announced it had been awarded a three-year, Indefinite Delivery Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) contract for Optically Improved Periscopes from DLA Land and Marine with a maximum potential value of $6.5 million and two additional option years. Production will be completed at our Optex Division of Optex Systems, Inc. in Richardson. | |
|
● | On December 10, 2024, the Company announced it had been awarded a new contract for Laser Filter Units and Window Assemblies supporting Night Vision devices utilized by the U.S. Armed Forces. The order value is $2.0 million with deliveries covering March 2025 through February 2026. Production will be completed at the Applied Optics Center Division of Optex Systems, Inc. |
| ● | On September 23, 2024, the Company announced it had been awarded contracts from two domestic customers for laser protected periscopes in support of ongoing armored vehicle production. The total value is $2.1 million with expected deliveries covering May 2025 through April 2026. Production will be completed at our Optex Division of Optex Systems, Inc. in Richardson. |
| ● | On July 8, 2024, the Company announced an award for a new contract for laser filter units supporting the XM-157 NGWS Scope. The order value is $2.5 million with deliveries covering August 2024 through July 2025. The products for this contract will be manufactured at the Applied Optics Center Division of Optex Systems, Inc. |
| ● | On May 6, 2024, the Company announced it had been awarded a new contract from a U.S. government prime contractor, for laser protected periscopes in support of the Armored Multi-Purpose Vehicle (AMPV). The order value is $3.8 million with deliveries covering November 2024 through March 2026. Production will be completed at our Optex Division of Optex Systems, Inc. in Richardson. |
| 4 |
| ● | On May 1, 2024, the Company announced a new contract from a U.S. government prime contractor, in support of a Night Vision Goggle Binocular program. The order value is $1.5 million with deliveries covering most of fiscal 2025. The products for this contract will be manufactured at the Applied Optics Center Division of Optex Systems, Inc. |
| ● | On April 16, 2024, the Company announced it had received an initial purchase order of $0.2 million for Laser Filter Assemblies supporting the new U.S. Military IVAS Program. The products for this contract will be manufactured at the Applied Optics Center Division of Optex Systems, Inc. with deliveries from April through October of 2024. |
| ● | On February 5, 2024, the Company announced a new five-year Indefinite Delivery Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) contract from the United States Defense Logistics Agency Land and Maritime for Sighting Systems for laser protected periscopes and vision blocks. The maximum value for the five-year IDIQ is estimated at $2.8 million. The award includes three base year, and two option years and will be completed at our Optex Division of Optex Systems, Inc. in Richardson. |
| ● | On November 14, 2023, the Company announced the award of a new contract from a U.S. Government Prime Contractor for Sighting Systems for $2.9 million. The Sighting Systems are critical in protecting armored vehicles fielded by the U.S. Military. These units will be manufactured at our Optex Division of Optex Systems, Inc. in Richardson. |
| ● | On November 13, 2023, the Company announced it was awarded a new laser filter unit contract from a U.S. Government Prime Contractor, in support of a visible sighting system. The order value is $1.3 million and the products for this contract will be manufactured at the Applied Optics Center Division of Optex Systems, Inc. | |
| ● | On October 18, 2023, the Company announced it was awarded a new laser filter unit contract from a U.S. Government Prime Contractor, in support of a visible sighting system. The order value is $1.1 million and the products for this contract will be manufactured at the Applied Optics Center Division of Optex Systems, Inc.
|
Products
Our products are installed on various types of U.S. military land vehicles, such as the Abrams, and Bradley and Stryker families of fighting vehicles, as well as light armored and armored security vehicles. We also manufacture and deliver numerous periscope configurations, rifle and surveillance sights and night vision optical assemblies. We deliver our products both directly to the federal government and to prime contractors.
In addition, the Company offers military specification (“mil-spec”) quality High Efficiency Anti-Reflective Coatings for Infrared applications in both the military and commercial markets. These coatings are manufactured at the Applied Optics Center (“AOC”) Division of the Company in Dallas, Texas.
We deliver high volume products, under multi-year contracts, to large defense contractors and government customers. Increased emphasis in the past several years has been on new opportunities to promote and deliver our products in foreign military sales, where U.S.-manufactured combat and wheeled vehicles are supplied (and upgraded) in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Defense. We have a reputation for quality and credibility with our customers as a strategic supplier. We also anticipate the opportunity to integrate some of our night vision and optical sights products into commercial applications.
Specific product categories by product line include:
| Product Line | Product Category | |
| Periscopes | Laser & Non-Laser Protected Plastic & Glass Periscopes, Electronic M17 Day/Thermal Periscopes, Vision Blocks | |
| Sighting Systems | Back Up Sights, Digital Day and Night Sighting Systems (“DDAN”), M36 Thermal Periscope, Unity Mirrors, Optical Weapon System Support and Maintenance (“OWSS”), Commander Weapon Station Sight (“CWSS”), Sight Assembly Refurbishment (“GOI MOD/Aquila”) | |
| Howitzers | M137 Telescope, M187 Mount, M119 Aiming Device, XM10 Aiming Circle |
| 5 |
| Other | Muzzle Reference Systems (“MRS”), Binoculars, Collimators, Speedtracker, Optical Lenses & Elements, Windows | |
| Applied Optics Center | Laser Interference Filter (“LIF”), Optical Assemblies, Laser Filter Units (“LFU”), Reticles, Day Windows, Binoculars, Specialty Thin Film Coatings. |
Contracts
Some of our contracts may allow for government contract financing in the form of contract progress payments pursuant to Federal Acquisition Regulation (“FAR”) 52.232-16, “Progress Payments”. Subject to certain limitations, this clause provides for government payment of up to 90% of incurred program costs prior to product delivery for small businesses like us. To the extent any contracts allow for progress payments and the respective contracts would result in significant preproduction cash requirements for design, process development, tooling, material or other resources which could exceed our current working capital or line of credit availability, we intend to utilize this benefit to minimize any potential negative impact on working capital prior to receipt of payment for the associated contract deliveries.
Our government contracts allow for FAR 52.243-1 which entitles the contractor to an “equitable adjustment” for contract or statement of work changes affecting cost or time of performance. In essence, an equitable price adjustment request is a request for a contract price modification (generally an increase) that allows for the contractor to be “made whole” for additional costs incurred which were necessitated by some modification of the contract effort. This modification may come from an overt change in U.S. Government requirements or scope, or it may come from a change in the conditions surrounding the contract (e.g., differing site conditions or late delivery of U.S. Government-furnished property) which result in statement of work additions, deletions, part substitutions, schedule or other changes to the contract which impact the contractor’s overall cost to complete.
Each contract with our customers has specific quantities of material that need to be purchased, assembled, and then shipped. Prior to bidding for a contract, we contact potential sources of material and receive qualified quotations for each material. In some cases, the entire volume is given to a single supplier and in other cases, the volume might be split between several suppliers. If a contract has a single source supplier and that supplier fails to meet their obligations (e.g., quality, delivery), then we would attempt to find an acceptable alternate supplier, and if successful, we would then renegotiate contractual deliverables (e.g., specifications, delivery or price). As of December 10, 2024, approximately 7% of our material requirements are single-sourced across 10 suppliers representing approximately 15% of our active supplier order values. Single-sourced component requirements span across all of our major product lines. Of these single-sourced components, we have material contracts (purchase orders) with firm pricing and delivery schedules in place with each of the suppliers to supply the parts necessary to satisfy our current contractual needs. See “Item 1.A. Risk Factors – Risks Relating to Our Business – Certain of our products are dependent on specialized sources of supply potentially subject to disruption which could have a material, adverse impact on our business” for a description of certain supplier risks we face, which description is incorporated herein by reference.
Approximately 96% of our contracts contain termination clauses for convenience. In the event these clauses should be invoked by our customer, future revenues against these contracts could be affected. However, these clauses allow for a full recovery of any incurred contract costs plus a reasonable fee up through and as a result of the contract termination. We are currently unaware of any pending terminations on our existing contracts.
In some cases, contract awards may be issued that are subject to renegotiation at a date (up to 180 days) subsequent to the initial award date. Generally, these subsequent negotiations have had an immaterial impact (0% to 5%) on the contract price of the affected contracts. Currently, none of our awarded contracts are subject to renegotiation.
We are subject to, and must comply with, various laws and governmental regulations that impact, among other things, our revenue, operating costs, profit margins and the internal organization and operation of our business. The material laws and regulations affecting our U.S. government business are summarized in the table below.
| 6 |
| Law/Regulation | Summary | |
| Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) | The principal set of rules is the Federal Acquisition Regulation System. This system consists of sets of regulations issued by agencies of the federal government of the United States to govern what is called the “acquisition process,” which is the process through which the government acquires goods and services. That process consists of three phases: (1) need recognition and acquisition planning, (2) contract formation, and (3) contract administration. This system regulates the activities of government personnel in carrying out that process. It does not regulate the purchasing activities of private sector firms, except to the extent that those activities involve government solicitations and contracts by reference. | |
| International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) | United States government regulations that control the export and import of defense-related articles and services on the United States Munitions List. These regulations implement the provisions of the Arms Export Control Act. | |
| Truth in Negotiations Act (TINA) | A public law enacted for the purpose of providing for full and fair disclosure by contractors in the conduct of negotiations with the government. The most significant provision included is the requirement that contractors submit certified cost and pricing data for negotiated procurements above a defined threshold of $2 million for contracts entered into after June 30, 2018. The law requires contractors to provide the government with an extremely broad range of cost or pricing information relevant to the expected costs of contract performance, and it requires contractors and subcontractors to submit cost or pricing data to the government and to certify that, to the best of their knowledge and belief, the data are current, accurate, and complete. A contracting officer may still request cost or price data, if necessary, without certification, to determine whether the proposed cost or price is fair and reasonable for contracts which are below the threshold. |
We are responsible for full compliance with the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR). Upon award, the contract may identify certain regulations that we need to meet. For example, a contract may allow progress billing pursuant to specific FAR clauses incorporated into the contract. Other contracts may call for specific first article acceptance and testing requirements. The FAR will identify the specific regulations that we must follow based on the type of contract awarded and contains guidelines and regulations for managing a contract after award, including conditions under which contracts may be terminated, in whole or in part, at the government’s convenience or for default. These regulations also subject us to financial audits and other reviews by the government of our costs, performance, accounting and general business practices relating to our government contracts, which may result in adjustment of our contract-related costs and fees and, among other things and impose accounting rules that define allowable and unallowable costs governing our right to reimbursement under certain contracts.
First Article Acceptance and Testing requirements consist of specific steps which could be comprehensive and time consuming. The dimensions and material specifications of each piece of the assembly must be verified, and some products may have in excess of 100 assembled parts. Once the individual piece parts are verified to be compliant to the specification, the assembly processes are documented and verified. A sample of the production (typically three units) is verified to meet final performance specifications. Once the units meet the final performance specification, they are then subjected to accelerated life testing, a series of tests which simulate the lifetime use of the product in the field. This consists of exposing the units to thermal extremes, humidity, mechanical shock, vibration, and other physical exposure tests. Once completed, the units undergo a final verification process to ensure that no damage has occurred as a result of the testing and that they continue to meet the performance specification. All of the information and data is recorded into a final first article inspection and test report and submitted to the customer along with the test units for final approval. First Article Acceptance and Testing is generally required on new contracts/product awards but may also be required on existing products or contracts where there has been a significant gap in production, or where the product has undergone significant manufacturing process, material, tooling, equipment or product configuration changes.
We are also subject to laws, regulations and executive orders restricting the use and dissemination of information deemed classified for national security purposes and the exportation of certain products and technical data as covered by the International Traffic in Arms Regulation (ITAR). In order to import or export items listed on the United States Munitions List, we are required to be registered with the Directorate of Defense Trade Controls office. The registration is valid for one year, and the registration fees are established based on the number of license applications submitted the previous year. We currently have an approved and current registration on file with the Directorate of Defense Trade Controls office. Once the registration is approved, each import/export license must be filed separately. License approval requires the company to provide proof of need, such as a valid contract or purchase order requirement for the specific product or technical data requested on the license and requires a detailed listing of the items requested for export/import, the end-user, the end-user statement, the value of the items, consignees/freight forwarders and a copy of a valid contract or purchase order from the end-user. The approval process for the license can vary from several weeks to six months or more. The licenses we currently use are the Department of State licenses: DSP-5 (permanent export), DSP-6 (license revisions) and DSP-73 (temporary export) and Department of Commerce: BIS-711 (export).
| 7 |
The above licenses are valid for 48 months from date that each license is issued. A summary of our active ITAR licenses is presented below (updated as of November 15, 2024):
| Fiscal Year | Number of | Total Contract Value of | ||||||||
| Active ITAR Licenses | of Expiration | Licenses | Licenses | |||||||
| DSP-5 | ||||||||||
| Issued 2021 | 2025 | 3 | $ | 232,630 | ||||||
| Issued 2022 | 2026 | 4 | 321,722 | |||||||
| Issued 2023 (none issued) | N/A | — | — | |||||||
| Issues 2024 | 2028 | 3 | 125,577 | |||||||
| Total DSP-5 Licenses | 10 | $ | 679,929 | |||||||
| DSP-6 (no active licenses) | N/A | — | $ | — | ||||||
| DSP-73 (no active licenses) | N/A | — | — | |||||||
| BIS-711 | ||||||||||
| Issued 2020 (expires December 31, 2024) | 2024 | 2 | 15,016 | |||||||
| Issued 2021 | 2025 | 4 | 323,911 | |||||||
| Issued 2022 | 2026 | 1 | 9,372 | |||||||
| Issued 2023 | 2027 | 10 | 1,359,344 | |||||||
| Issued 2024 | 2028 | 7 | 1,270,327 | |||||||
| Total BIS-711 Licenses | 24 | $ | 2,977,970 | |||||||
| Total All Licenses | 34 | $ | 3,657,899 | |||||||
These licenses are subject to termination if a licensee is found to be in violation of the Arms Export Control Act or the ITAR requirements. If a licensee is found to be in violation, in addition to a termination of its licenses, it can be subject to fines and penalties by the government.
Our contracts may also be governed by the Truth in Negotiation Act (TINA) requirements where certain of our contracts or proposals exceed the TINA threshold ($2 million for awards after June 30, 2018), and/or are deemed as sole source, or non-competitive awards, covered under this act. For these contracts, we must provide a vast array of cost and pricing data in addition to certification that our pricing data and disclosure materials are current, accurate and complete upon conclusion of the negotiation. Due to the additional disclosure and certification requirements, if a post contract award audit were to uncover that the pricing data provided was in any way not current, accurate or complete as of the certification date, we could be subjected to a defective pricing claim adjustment with accrued interest. We have no history of defective pricing claim adjustments and have no outstanding defective pricing claims pending. Additionally, as a result of this requirement, contract price negotiations may span from two to six months and can result in undefinitized or not to exceed ceiling priced contracts subject to future downward negotiations and price adjustments. Currently, we do not have any undefinitized contracts subject to further price negotiation.
Our
failure to comply with applicable regulations, rules and approvals or misconduct by any of our employees could result in the imposition
of fines and penalties, the loss of security clearances, the loss of our U.S. government contracts or our suspension or debarment from
contracting with the U.S. government generally, any of which could have a material adverse effect our business, financial condition,
results of operations and cash flows. We are currently in compliance with all applicable regulations and do not have any pending claims
as a result of noncompliance.
| 8 |
The terms of our significant contracts with a total award value of more than $1.0 million as of December 9, 2024, are as follows:
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Customer | Contract/PO | Product | Type | Award | Backlog | Delivery Period | |||||||||||
| OPX | U.S. Prime Contractor(1) | PO 35515590 | Sighting Systems | FFPQ | $ | 4.6 | $ | 1.3 | Dec 2024 - Mar 2027 | |||||||||
| OPX | DLA Land and Maritime(2) | SPE7LX19D0089 | Periscopes | IDIQ | 1.7 | 0.7 | Dec 2024 - Nov 2025 | |||||||||||
| OPX | U.S. Prime Contractor(3) | PO 63659 | XM10 Aiming Circles | FFPQ | 2.3 | 2.3 | Estimated 2026 | |||||||||||
| OPX | DLA Land and Maritime(4) | SPE7LX21D0057 | Periscopes | IDIQ | 7.4 | 2.5 | Dec 2024 - Jun 2025 | |||||||||||
| OPX | Government of Israel MOD(5) | PO 40385578 | Refurbish Night Vision Equipment | FFPQ | 3.1 | 2.3 | 2025 - 2026 | |||||||||||
| OPX | DLA Land and Maritime(6) | SPE7LX23D0092 | Periscopes | IDIQ | 2.0 | 1.1 | Dec 2024 - Oct 2025 | |||||||||||
| OPX | U.S. Prime Contractor(7) | PO 40431189 | Periscopes | FFPQ | 1.9 | 1.3 | Dec 2024 - Nov 2025 | |||||||||||
| OPX | U.S. Prime Contractor(8) | PO 40431702 | Collimators | FFPQ | 1.3 | 1.3 | Jul 2025 - Mar 2027 | |||||||||||
| OPX | U.S. Prime Contractor(9) | PO 363920 | Periscopes | FFPQ | 3.7 | 3.6 | Dec 2024 - Mar 2026 | |||||||||||
| OPX | U.S. Prime Contractor(10) | PO 1402471 | Periscopes | FFPQ | 1.2 | 1.2 | Mar 2025 | |||||||||||
| AOC | U.S. Prime Contractor(11) | PO 40385578 | Day Windows | IDIQ | 2.9 | 1.0 | Dec 2024 - Nov 2025 | |||||||||||
| AOC | DLA Land at Aberdeen(12) | SPRBL123D0001 | Light Interference Filters | IDIQ | 4.2 | 2.2 | Dec 2024 - Dec 2025 | |||||||||||
| AOC | U.S. Prime Contractor(13) | PO 4500045346 | Laser Filter Units | FFPQ | 1.1 | 0.5 | Dec 2024 - June 2025 | |||||||||||
| AOC | U.S. Prime Contractor(14) | PO 921424 | Light Interference Filters | FFPQ | 1.1 | 1.1 | Dec 2024 - Sept 2025 | |||||||||||
| AOC | U.S. Prime Contractor(15) | PO 244 | Laser Filter Units | FFPQ | 2.5 | 1.7 | Dec 2024 - Jul 2025 | |||||||||||
| (1) | The original three-year subcontract was awarded on September 11, 2017 to provide LAV 6.0 optimized weapon system support for Optex’s Commander Sighting System. The contract includes option years to extend the period of performance through 2035 if awarded. The current contract option extends the in-service support through March 2027 for their existing fleet of Light Armored Vehicles. |
| (2) | Prime contract awarded March 4, 2019. This is a long-term, Indefinite Delivery Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) Contract with firm fixed pricing for the duration of a base period of three (3) years plus two (2) firm fixed priced option years for a potential total of (5) five years. On February 27, 2023, the customer exercised the second of two option years extending the ordering period of the contract through March 3, 2024. |
| (3) | Subcontract purchase order by a U.S. prime contractor in support of government contract W15QKN-16-D-0055 for Aiming Circle optical subassemblies. The purchase order was awarded on July 30, 2020 for $2 million and amended to $2.3 million on September 14, 2020 and includes non-recurring engineering, first article testing and production deliveries. Contract has been delayed pending receipt of customer furnished material and is pending changes to the contract delivery schedule. |
| (4) | Prime contract awarded on January 6, 2021. This is a long-term, Indefinite Delivery Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) Contract with firm fixed pricing for the duration of a base period of three (3) years plus two (2) firm fixed priced option years for a potential total of (5) five years for periscopes valued up to $14.4 million. On October 7, 2024, option two was exercised by DLA, extending the ordering period from January 6, 2025 through January 5, 2026. |
| 9 |
| (5) | Foreign Military Sales purchase orders awarded October 27, 2022 to repair and refurbish night vision equipment for the Government of Israel which includes an option for an additional quantity up to 100%. Deliveries began December 2023 and are expected to continue through 2026 pending receipt of customer units for refurbishment. |
| (6) | Prime contract awarded on June 27, 2023. This is a long-term, Indefinite Delivery Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) Contract with firm fixed pricing for the duration of a base period of three (3) years plus two (2) firm fixed priced option years for a potential total of (5) five years for periscopes. The award has a maximum order value of $2.1 million. |
| (7) | Subcontract purchase order awarded on November 10, 2023 by a U.S. prime contractor in support of U.S. government contracts. |
| (8) | Subcontract purchase order awarded on November 6, 2023 by a U.S. prime contractor in support of U.S. government contracts. |
| (9) | Subcontract purchase order awarded on April 24, 2024 by a U.S. prime contractor in support of U.S. government contracts. |
| (10) | Subcontract purchase order awarded on September 20, 2024 by a U.S. prime contractor in support of U.S. government contracts. |
| (11) | Subcontract purchase order originally awarded August 29, 2021 with multiple revisions and additions through November 15, 2024. |
| (12) | Prime contract awarded on November 2, 2022 for spare Light Interference Filters associated with various Night Vision Goggle systems. This is a five-year Indefinite Delivery Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) Contract with firm fixed pricing for the duration of the contract. The award has a maximum order value of $7.5 million. |
| (13) | Subcontract purchase order awarded on October 16, 2023 by a U.S. prime contractor in support of U.S. government contracts. |
| (14) | Subcontract purchase order awarded on April 30, 2024 by a U.S. prime contractor in support of U.S. government contracts. |
| (15) | Subcontract purchase order awarded on July 8, 2024 by a U.S. prime contractor in support of U.S. government contracts. |
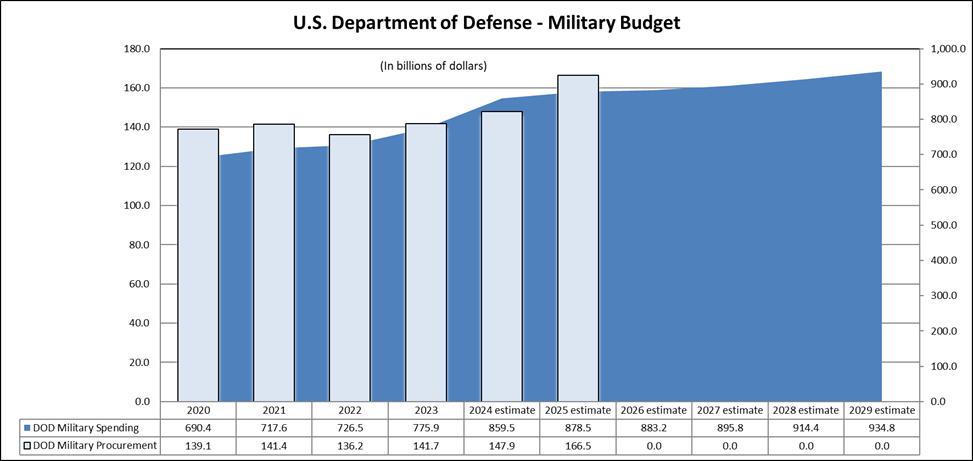
Market Opportunity — U.S. Military
During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, approximately 84% of our business was in support of U.S. military products. The chart below was derived from public government spending sources and depicts total U.S. military spending from 2020 through 2023 and estimated spending through 2029. The purpose of including this chart is to provide the reader with historical trend data and projected U.S. military defense and procurement spending over time. However, the Company cannot provide any assurances that the historical trend data is predictive of future spending.
For fiscal year 2025, the Government Publishing Office (GPO) projects total military spending at $878.5 billion, an overall increase of 2.2% over estimated 2024 spending. The chart below also depicts the GPO’s projection of increased spending through 2029 of 6.4% from the 2025 plan level, reflecting an average increase of 1.6% per year for years 2026 through 2029. For military procurement spending, a subset of total military spending, the GPO projects an overall increase of $18.6 billion, or 12.6%, in fiscal year 2025 as compared to the estimated spending in fiscal year 2024.
The National Defense Authorization Act (“NDAA”) for Fiscal Year 2025 current request of $895 billion has not yet been enacted by Congress in 2024. The 2025 fiscal year request represents an increase of $11.3 billion, or 1.3% over the prior year NDAA of $883.7 billion. The chart below depicts the original estimated funding levels from the U.S. Department of Defense based on the Fiscal Year 2025 budget request.
| 10 |

Source: Government Publishing Office, U.S. Budget Historical Tables, FY 2025, Table 3.2 Outlays by function and sub function, 1962-2029.
The table below depicts the U.S. Department of Defense (“DoD”) budget request for fiscal year 2025 for major ground system programs. The last five years have experienced a significant reduction in spending for U.S ground system military programs, and more specifically on the Abrams Tank Modifications/Upgrades, which has a direct impact on the Optex Systems Richardson segment revenue. The total fiscal year 2025 budget request for major ground system programs decreased by 4.7% from the fiscal year 2024 levels and by 27.2% from the fiscal year 2023 levels. Although it is difficult to directly tie the budget request to specific components provided by Optex Systems, we provide periscopes, collimator assemblies, vision blocks and laser interface filters to the U.S. armed forces on almost all of the ground system platforms categorized below.
| ($ in Millions) | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | FY2025 | |||||||||||||||
| Joint Light Tactical Vehicle | $ | 1,408.3 | $ | 1,046.6 | $ | 1,429.7 | $ | 1,191.8 | $ | 1,179.5 | ||||||||||
| ARMY | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Abrams Tank Modification/Upgrade | 1,404.2 | 1,264.3 | 1,297.7 | 896.5 | 1,020.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Armored Multi-Purpose Vehicle | 132.1 | 984.6 | 1,237.0 | 567.1 | 527.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Paladin Integrated Management | 681.4 | 662.9 | 1,026.8 | 511.6 | 460.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Family of Medium Tactical Vehicles | 211.2 | 144.4 | 233.9 | 142.9 | 153.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Family Of Heavy Tactical Vehicles | 28.8 | 214.0 | 326.3 | 110.6 | 148.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Next Generation Squad Weapon | 125.3 | 127.6 | 199.6 | 328.1 | 389.4 | |||||||||||||||
| XM30 Combat Vehicle | - | 194.9 | 519.1 | 996.7 | 504.8 | |||||||||||||||
| M10 Booker (Mobile Protected Firepower) | - | - | 410.5 | 496.8 | 508.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Stryker | 1,186.3 | 1,112.7 | 1,275.0 | 639.1 | 469.4 | |||||||||||||||
| USMC | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Amphibious Combat Vehicle | 478.1 | 591.9 | 605.4 | 660.8 | 870.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Total Ground Systems Vehicles (millions) | $ | 5,655.7 | $ | 6,343.9 | $ | 8,561.0 | $ | 6,542.0 | $ | 6,232.8 | ||||||||||
Source: Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)/Chief Financial Officer, “Program Acquisition Cost by Weapon System, United States Department of Defense, Fiscal Year 2025 Budget Request”, March 2024 and “Program Acquisition Cost by Weapon System, United States Department of Defense, Fiscal Year 2024 Budget Request”, April 2023 and “Program Acquisition Cost by Weapon System, United States Department of Defense, Fiscal Year 2023 Budget Request”, May 2022.
| 11 |
The 2025 Department of Defense Budget indicates an overall decrease in ground system vehicle program spending in the fiscal year 2024 and 2025 appropriation budget years from fiscal year 2023. There is generally a six- to eighteen-month delay between U.S. defense budget requests and program delivery orders related to our products from government agencies and our prime defense customers. In addition, DoD budget requests are often changed throughout the congressional NDAA Budgeting and Budget appropriations process. The DoD budget requests exclude any foreign military sales as they are funded separately from the annual NDAA budgets. We are carefully watching the projected trends in both DoD military spending and FMS as defense allocation priorities change, as well as challenges which are presented from the global recession and changes in political climate to ascertain any potential impact to the Company’s future revenue.
The Applied Optics Center supports numerous other military platforms outside of the ground system vehicles budget, such as infantry rifle scopes, night vision monoculars, infantry and navy binoculars, night goggles, and infrared aircraft filters. The Applied Optics Center has seen a substantial increase in orders from new and existing customers in support of the other platforms, which we expect to offset the impact of the ground systems reductions to their base revenue.
Market Opportunity — Foreign Military
Our products directly support FMS combat vehicles globally, including Canada, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Morocco, Egypt, South America, and Israel. We have increased efforts to promote our proven military products, as well as newly improved product solutions directly to foreign military representatives and domestic defense contractors supporting the FMS initiatives.
We were successful with the Israeli Ministry of Defense (“IMOD”) in refurbishing a small quantity of their Night Vision Rifle Scopes. Given this success, in November 2022, the IMOD awarded us a $3.4 million follow on contract to continue this activity through 2026. We began deliveries against the contract during the first quarter of fiscal year 2024. If we successfully execute this contract, we would expect another contract award of similar size and duration.
We are also exploring possibilities to adapt some of our products for commercial use in those markets that demonstrate potential for solid revenue growth, both domestically and internationally.
Market Opportunity — Commercial
Our products are currently sold to military and related government markets. We believe there may be opportunities to commercialize various products we presently manufacture to address other markets. Our initial focus will be directed in four product areas.
| ● | Big Eye Binoculars — While the military application we produce is based on mature military designs, we own all castings, tooling and glass technology. These large fixed mount binoculars could be sold to cruise ships, personal yachts and cities/municipalities. The binoculars are also applicable to fixed, land-based outposts for private commercial security as well as border patrols and regional law enforcement. | |
| ● | Thin Film Coatings — The acquisition of the Applied Optics Center also creates a new sector of opportunity for commercial products for us. Globally, commercial optical products use thin film coatings to create product differentiation. These coatings can be used for redirecting light (mirrors), blocking light (laser protection), absorbing select light (desired wavelengths), and many other combinations. They are used in telescopes, rifle scopes, binoculars, microscopes, range finders, protective eyewear, photography, etc. Given this broad potential, the commercial applications are a key opportunity going forward. | |
| ● | Optical Assemblies – Through the Applied Optics Center, we are utilizing our experience in military sighting systems to pursue commercial opportunities associated with products that incorporate multi-lens optical cell assemblies, bonded optical elements and mechanical assemblies. There are a wide variety of products in the medical, machine vision, automotive and outdoor recreation fields that can benefit from our capabilities. Support to domestic customers for these type products has driven significant increases in Applied Optics Segment sales during the last five years. | |
| ● | Optex Outdoors – This launch brings military-grade optical technology directly to civilian marksmen and extreme long-range competitors, expanding Optex’s reach beyond its traditional military market. The Optex Outdoors webstore offers a curated selection of advanced optical products, including riflescope prisms, chronographs, and stabilized viewing products—designed specifically for the needs of elite shooters and outdoor enthusiasts. Each product is engineered and built in Richardson, Texas. |
| 12 |
Customer Base
We serve customers in four primary categories: as prime defense contractor (Defense Logistics Agency (“DLA”) Land and Maritime, DLA Warren, DLA Aviation, U.S. Army, Navy and Marine Corps), as defense subcontractor (General Dynamics, L-3 Communications, Elbit Systems, BAE, Sig Sauer, Enterprise Cabling and Vortex Optics), as a military supplier to foreign governments (Israel, Australia, South America and Canada) and as a commercial optical assembly supplier (Nightforce Optics, Gables Engineering). During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, we derived approximately 77% of our gross business revenue from six major customers: U.S. government agencies (20%), four U.S. defense contractors (25%, 7%, 6% and 6%) and one major commercial customer (13%). We have approximately 150 discrete contracts for items that are utilized in vehicles, optical product lines and as spare parts. Due to the high percentage of prime and subcontracted U.S. defense revenues, large customer size and the fact that there are multiple contracts with each entity, which are not interdependent, we are of the opinion that this provides us with a fairly well diversified revenue pool.
Marketing Plan
We believe we are well positioned to service both U.S. and foreign military needs by our focus on delivering products that satisfy the following factors important to the U.S. military:
| ● | Product reliability — failure can cost lives | |
| ● | Speed to delivery and adherence to delivery schedule | |
| ● | System life cycle extension | |
| ● | Low cost/best value | |
| ● | Visual aids for successful execution of mission objectives | |
| ● | Mission critical products specifically related to soldier safety. |
| 13 |
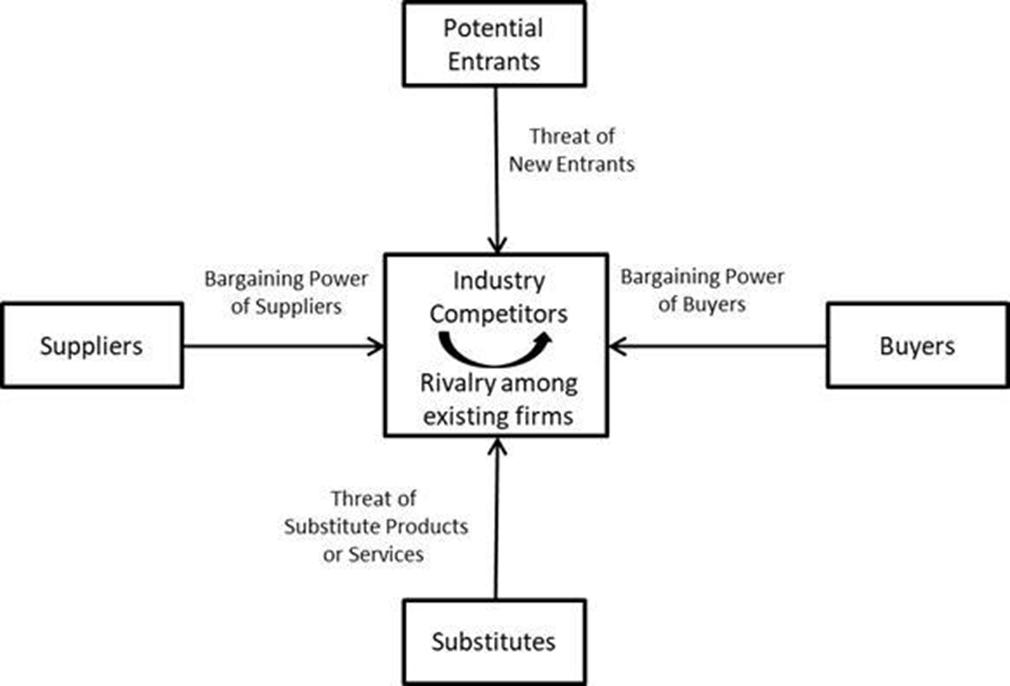
Potential Entrants — Low Risk to us. In order to enter this market, potential competitors must overcome several barriers to entry. The first hurdle is that an entrant would need to prove to the government agency in question the existence of a government approved accounting system for larger contracts. Second, the entrant would need to develop the processes required to produce the product. Third, the entrant would then need to produce the product and submit successful test requirements (many of which require lengthy government consultation for completion). Finally, in many cases, the customer has an immediate need and therefore cannot wait for this qualification cycle and therefore must issue the contracts to existing suppliers. Given the expense and time commitment of development and qualification testing, the barrier to entry is high for new competitors.
Buyers — Medium Risk to us. In most cases the buyers (usually government agencies or defense contractors) have two fairly strong suppliers. It is in their best interest to keep at least two, and therefore, in some cases, the contracts are split between suppliers. In the case of larger contracts, the customer can request an open book policy on costs and expects a reasonable margin to have been applied.
Substitutes — Low Risk to us. We have both new vehicle contracts and replacement part contracts for the same product. Three combat vehicles have a long history of service in the U.S. Army. The first M-1 Abrams Tank entered service with the Army in 1980; the M-2/M-3 Bradley Fighting Vehicle in 1981; and the Stryker Combat Vehicle in 2001. Since it was first fielded in 1980, the Abrams tank has undergone near-continuous upgrades and improvements and is the principal battle tank of the United States Army and Marine Corps, and the armies of Egypt, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Iraq and Australia. On average, there has been a new improvement package every seven years. The XM30 Mechanized Infantry Combat Vehicle, formerly known as the Optionally Manned Combat Vehicle, is the U.S. Army’s sixth attempt to replace the Bradley fighting vehicle. The latest Army “light tank” is the M10 Booker Combat Vehicle, formerly known as the Mobile Protected Firepower System, and is much smaller than the Abrams main battle tank. The Abrams, XM30, M10 Booker and Stryker vehicles are the only tanks currently in production by the government. Optex Systems provides periscopes and optical sighting systems in support of all four vehicle platforms. We expect that these tanks will continue to be used through approximately 2040.
Suppliers — Low to Medium Risk to Optex Systems Holdings. The suppliers of standard processes (e.g., casting, machining and plating) need to be very competitive to gain and/or maintain contracts. Those suppliers of products that use top secret clearance processes have a slight advantage; however, there continues to be multiple avenues of supply and therefore only moderate power.
Consistent with our marketing plan and business model, the AOC acquisition strengthened our overall position by decreasing the bargaining power of their suppliers through the backwards integration of a key supplier and created additional barriers of entry for potential competitors.
The following matrix reflects the current focus of our four basic approaches for sales and development:
| 1) | Sell existing products to existing customers. | |
| 2) | Sell existing products to new customers. | |
| 3) | Develop new products to meet the needs of our existing customers. | |
| 4) | Develop new products to meet the needs of new customers. |
| Existing Customers | New Customers | |||
| New Products | US Army Central Command - Binoculars GDLS - DDAN, OWSS |
Israel - GOI MOD/Aquila U.S. Prime Contractor - XM10 Aiming Circle | ||
Commercial - Optical Lens Reticles |
Commercial - Optical Lens, Spotting Scopes, Monocular Lens, Chronographs, Optical Wedges | |||
| Existing Products | US Army Central Command - Periscopes, Back Up Sights, | Commercial - Optical Lens, Spotting Scopes Monocular Lens | ||
| Binoculars, Vision Blocks, | ||||
| Laser Filter Units | U.S. Prime Contractor – Laser Filter Units | |||
| GDLS - Periscopes, Collimators | ||||
| BAE - Periscopes | ||||
| L3 - Laser Interface Filters | ||||
| DLA - Optical Elements |
| 14 |
Operations Plan
Our operations plan can be broken down into three distinct areas: material management, manufacturing space planning and efficiencies associated with economies of scale.
Materials Management
The largest portion of our costs is materials. Our continuous improvements to effectively manage material costs include the following activities:
| - | Successful completion of annual surveillance audit for ISO 9001:2008 certificate, with no major nonconformance issues | |
| - | Weekly cycle counts on inventory items | |
| - | Weekly material review board meeting on non-moving piece parts | |
| - | Kanban kitting on products with consistent ship weekly ship quantities | |
| - | Daily cross functional floor meetings focused on delivery, yields and labor savings | |
| - | Redesigned floor layout using tenant improvement funds | |
| - | Daily review of yields and product velocity | |
| - | Bill of material reviews prior to work order release
| |
| - | Supplier management and notification tools for on time delivery and quality tracking |
Future continuous improvement opportunities include the full implementation and training of the shop floor control module within our ERP system. We have begun testing and implementation within selected process.
Manufacturing Space Planning
We currently lease 93,967 square feet of manufacturing space (see “Properties”). Our current facilities are sufficient to meet our immediate production needs without excess capacity. As our processes are primarily labor driven, we are able to easily adapt to changes in customer demand by adjusting headcounts, overtime schedules and shifts in line with production needs. In the event additional floor space is required to accommodate new contracts, Optex has the option to lease adjacent floor space at the current negotiated lease cost per square foot. Consistent with the space planning, we will drive economies of scale to reduce support costs on a percentage of sales basis. These cost reductions can then be either passed through directly to the bottom line or used for business investment.
Our manufacturing process is driven by the use of six sigma techniques and process standardization. Our activities in this area have included the use of six sigma projects in several production areas which has led to improved output and customer approval on the aesthetics of the work environment. In addition, we use many tools including 5S programs, six sigma processes, and define, measure, analyze, improve, control (DMAIC) problem solving techniques, to identify bottlenecks within the process flow, reduce cost and improve product yields. Successful results can then be replicated across the production floor and drive operational improvements.
| 15 |
Economies of Scale
Plant efficiencies fluctuate as a function of program longevity, complexity and overall production volume. Our internal processes are primarily direct labor intensive and can be more easily adapted to meet fluctuations in customer demand; however, our material purchases, subcontracted operations and manufacturing support costs are extremely sensitive to changes in volume. As our volume increases, our support labor, material and scrap costs decline as a percentage of revenue as we are able to obtain better material pricing, and scrap, start up and support labor (fixed) costs and they are spread across a higher volume base. Conversely, as production volumes decline, our labor and material costs per unit of production generally increase. Additional factors that contribute to economies of scale relate to the longevity of the program. Long running, less complex programs (e.g., periscopes) do not experience as significant of an impact on labor costs as production volumes change, as the associated workforce is generally less specialized and can be ramped quickly as headcounts shift. Our more complex thin laser filter coatings, Howitzer and thermal day/night programs are more significantly impacted by volume changes as they require a highly specialized workforce and ramp time is longer as the training is more complex. We continually monitor customer demand over a rolling twelve-month window and in order to anticipate any changes in necessary manpower and material which allows us to capitalize on any benefits associated with increased volume and minimize any negative impact associated with potential declines in product quantities.
Sources and Availability of Raw Materials
Disclosure responsive to this item is incorporated herein by reference to “Risk Factors – Risks Related to Our Business – Certain of our products are dependent on specialized sources of supply potentially subject to disruption which could have a material, adverse impact on our business.”
Intellectual Property
Trade Secrets and Know-How
We utilize several highly specialized and unique processes in the manufacture of our products. While we believe that these trade secrets have value, it is probable that our future success will depend primarily on the innovation, technical expertise, manufacturing and marketing abilities of our personnel. We cannot assure you that we will be able to maintain the confidentiality of our trade secrets or that our non-disclosure agreements will provide meaningful protection of our trade secrets, know-how or other proprietary information in the event of any unauthorized use, misappropriation or other disclosure. The confidentiality agreements that are designed to protect our trade secrets could be breached, and we might not have adequate remedies for the breach. Additionally, our trade secrets and proprietary know-how might otherwise become known or be independently discovered by others.
Patents
We possess three utility patents and three design patents. We have filed two new patent applications which are currently under review at the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. These are for an Improved Next Shot Compensation System for Weapons (patent application number 18651580) and a Laser Filter Antenna (patent application number 18809740).
The following patents generally expire 20 years after issuance.
On April 4, 2023, we were issued U.S. Patent No. 11,619,824 B2 titled “Selectable Offset Image Wedge” which is a mechanical wedge used to offset the image anywhere in the selectable range of circular travel within the defined offset field of view. This application is a continuation-in-part of U.S. Patent No. 10,324,298 and claims priority to U.S. Patent No. 10,324,298, issued on June 18, 2019.
On November 4, 2021 we were issued U.S. Patent No. 2021/0341746A1 titled “Selectable Offset Image Wedge” which is a mechanical wedge used to offset the image anywhere in the selectable range of circular travel within the defined offset field of view. This application is a continuation-in-part of U.S. Patent No. 10,324,298 and claims priority to U.S. Patent No. 10,324,298, issued on June 18, 2019.
On June 18, 2019 we were issued U.S. Patent No. 10,324,298 titled “Offset Image Wedge with Dual Capability and Alignment Technique”. The invention relates to an offset image wedge for use on a bore-sighted rifle mounted directly onto the scope via a clamp mounting device. The wedge allows for a dual image which can be aligned in the field and provides the user with a choice of either a bore-sighted image or an offset image without removing the wedge.
On July 11, 2017, we were issued U.S. Patent No. D791,852 S, for our Red Tail Digital Spotting Scope. We have a retail sales relationship with Cabela’s Inc. and Amazon, to distribute these scopes. They are currently the only digital spotting scope offered by Cabela’s. Our Red Tail Digital Spotting Scopes also received a favorable review from Trigger Magazine in 2017.
In May 2015, we announced the issuance to us of U.S. Patent No. 13,792,297 titled “ICWS Periscope”. This invention improves previously accepted levels of periscope performance that, in turn, improve soldier’s safety.
| 16 |
In December 2013, Optex Systems, Inc. was issued U.S. Patent No. 23,357,802 titled “Multiple Spectral Single Image Sighting System Using Single Objective Lens Set.” The technology platform, designed for our DDAN program, is applicable to all ground combat vehicles used by the US and foreign militaries. This invention presents a single image to both day and night sensors using precision optics, which in turn allows the user to individually observe day, night, or day and night simultaneously. In addition, it has proven to be especially useful in light transition points experienced at dusk and dawn. We are in production and currently delivering sighting systems with this advanced technology, a significant upgrade in the goal of supporting our customers as they modernize the worldwide inventory of aging armored vehicles. This technology is applicable to many sighting systems, and it has already been designed for implementation on the Light Armored Vehicles, the Armored Security Vehicle, the Amphibious Assault Vehicle, and the M60 Main Battle Tank. DDAN technology has advanced the capabilities of these installed weapon systems and is the first in a series of patents we have applied for to protect our Intellectual Property portfolio in support of the warfighters who use these systems.
Licenses
In May 2012, we purchased a perpetual, non-exclusive license, with a single up-front license fee of $200,000 to use Patent 7,880,792 “Optical and Infrared Periscope with Display Monitor” (issued in 2011 and owned by Synergy International Optronics, LLC). We believe the purchase of the license agreement may allow us to extend and expand our market potential for the M113APC vehicle type which has the highest number of commonly used armored vehicles in the world. The current estimated active M113 APC worldwide inventory is over 80,000 units. This licensing of this patent allows us to develop additional products for this vehicle type, including the M17 Day/Thermal and M17 Day/Night periscopes. We are actively marketing the new periscopes internationally and completed our first international shipment utilizing this technology in March 2014. We continue to prototype these products and demonstrate them to potential customers.
Our competitors, many of which have substantially greater resources, may have applied for or obtained, or may in the future apply for and obtain, patents that will prevent, limit or interfere with our ability to make and sell some of our products. Although we believe that our products do not infringe on the patents or other proprietary rights of third parties, we cannot assure you that third parties will not assert infringement claims against us or that such claims will not be successful.
Competition
The markets for our products are competitive. We compete primarily on the basis of our ability to design and engineer products to meet performance specifications set by our customers. Our customers include military and government end users as well as prime contractors that purchase component parts or subassemblies, which they incorporate into their end products. Product pricing, quality, customer support, experience, reputation and financial stability are also important competitive factors.
There are a limited number of competitors in each of the markets for the various types of products that we design, manufacture and sell. At this time, we consider our primary competitors for the Optex Systems Richardson site to be Gus Periscopes. The Applied Optics Center thin film and laser coatings products compete primarily with Materion-Barr, Artemis and Alluxa.
Our competitors are often well entrenched, particularly in the defense markets. While we believe that the quality of our technologies and product offerings provides us with a competitive advantage over certain manufacturers, some of our competitors have substantially greater financial and other resources than we do to spend on the research and development of their technologies and for funding the construction and operation of commercial scale plants.
We expect our competitors to continue to improve the design and performance of their products. We cannot assure investors that our competitors will not develop enhancements to, or future generations of, competitive products that will offer superior price or performance features, or that new technology or processes will not emerge that render our products less competitive or obsolete. Increased competitive pressure could lead to lower prices for our products, thereby adversely affecting our business, financial condition and results of operations. Also, competitive pressures may force us to implement new technologies at a substantial cost, and we may not be able to successfully develop or expend the financial resources necessary to acquire new technology. We cannot assure you that we will be able to compete successfully in the future.
| 17 |
Employees and Human Capital
We had 128 full time equivalent employees as of September 29, 2024, which include a small temporary work force to handle peak loads as needed. We are in compliance with local prevailing wage, contractor licensing and insurance regulations, and have good relations with our employees, who are not currently unionized. We use outside consultants for various services. We have not experienced any work stoppages and are not a party to a collective bargaining agreement. Management considers labor relations to be good.
We are dedicated to preserving operational excellence and remaining an employer of choice. We provide and maintain a work environment that is designed to attract, develop and retain top talent through offering our employees an engaging work experience that contributes to their career development. We recognize that our success is based on the collective talents and dedication of those we employ, and we are highly invested in their success. We value our employees and believe that employee loyalty and enthusiasm are key elements of our operating performance.
Corporate History
Optex Systems Holdings, Inc. is a Delaware corporation originally organized in Delaware as Sustut Exploration, Inc. in April 2006. Optex Systems, Inc. is a Delaware corporation organized in September 2008. In March 2009, Optex Systems, Inc. engaged in a reverse merger with Sustut Exploration, Inc., in connection with which the latter was renamed Optex Systems Holdings, Inc. and the former became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Optex Systems Holdings, Inc.
Internet Address
The Company maintains an internet website at the following address: www.optexsys.com. The information on the Company’s website is not incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. Prospective investors should carefully consider the risks described below, together with all of the other information included or referred to in this Annual Report, before purchasing shares of our common stock. There are numerous and varied risks, known and unknown, that may prevent us from achieving our goals. The risks described below are not the only risks we face. If any of these risks actually materializes, our business, financial condition or results of operations may be materially adversely affected. In such case, the trading price of our common stock could decline and investors in our common stock could lose all or part of their investment. The risks and uncertainties described below are not exclusive and are intended to reflect the material risks that are specific to us, our industry and companies that have securities trading on an over-the-counter market.
Risks Related to our Business
Our results of operations could be adversely affected by economic and political conditions globally and the effects of these conditions on our customers’ businesses and levels of business activity.
Economic and political events in the past few years have altered the landscape in which we and other U.S. companies operate in a variety of ways. In response to inflationary pressures, between January 2022 and July 2023, the U.S. Federal Reserve incrementally raised interest rates, resulting in an increase in the cost of borrowing for us, our customers, our suppliers, and other companies relying on debt financing. World events, such as the Russian invasion of Ukraine and the resulting economic sanctions, have impacted the global economy, including by exacerbating inflationary and other pressures linked to COVID-related supply chain disruptions. In addition, the threat of a larger war in the Middle East after the Hamas terrorist attacks on Israel could affect oil prices and have other, potentially recessionary, effects on the global economy. Prolonged inflationary conditions and prolonged periods of high interest rates could further negatively affect U.S. and international commerce and exacerbate or prolong the period of high energy prices and supply chain constraints. At this time, the extent and duration of these economic and political events and their effects on the economy and the Company are impossible to predict.
| 18 |
Our historical operations depend on government contracts and subcontracts. We face risks related to contracting with the federal government, including federal budget issues and fixed price contracts.
Future general political and economic conditions, which cannot be accurately predicted, may directly and indirectly affect the quantity and allocation of expenditures by federal agencies and foreign governments. Even the timing of incremental funding commitments to existing, but partially funded, contracts can be affected by these factors. Therefore, cutbacks or re-allocations in the federal or foreign government budgets could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations. Obtaining government contracts may also involve long purchase and payment cycles, competitive bidding, qualification requirements, delays or changes in funding, budgetary constraints, political agendas, extensive specification development, price negotiations and milestone requirements. In addition, our government contracts are primarily fixed price contracts, which may prevent us from recovering costs incurred in excess of budgeted costs. Fixed price contracts require us to estimate the total project cost based on preliminary projections of the project’s requirements. The financial viability of any given project depends in large part on our ability to estimate such costs accurately and complete the project on a timely basis. Some of those contracts are for products that are new to our business and are thus subject to unanticipated impacts to manufacturing costs. Even if our estimates are reasonable at the time made, prices of materials are subject to unanticipated adverse fluctuation, and are affected by inflationary pressures. In the event our actual costs exceed the fixed costs determined under our product contracts, we will not be able to recover the excess costs which could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations. We examine these contracts on a regular basis and accrue for anticipated losses on these contracts, if necessary.
We have several multiyear IDIQ contracts at fixed prices which have open ordering periods and are currently at low profit rates or in a loss condition. These contracts are typically three-year IDIQ contracts with two optional award years, and as such, we are obligated to accept new task awards against these contracts until the contract expiration. Should contract costs continue to increase above the negotiated selling price, or in the event the customer should release substantial quantities against these existing loss contracts, the losses could be material. For contracts currently in a loss status based on the estimated per unit contract costs, losses are booked immediately on new task order awards. As of September 29, 2024, there was $259 thousand in accrued loss provisions for loss contracts or cost overruns.
Approximately 96% of our contracts contain termination clauses for convenience. In the event these clauses should be invoked by our customer, future revenues against these contracts could be affected. However these clauses allow for a full recovery of any incurred contract costs plus a reasonable fee up through and as a result of the contract termination. We are currently unaware of any pending terminations on our existing contracts.
In some cases, contract awards may be issued that are subject to renegotiation at a date (up to 180 days) subsequent to the initial award date. Generally, these subsequent negotiations have had an immaterial impact (zero to 5%) on the contract price of the affected contracts. Currently, none of our awarded contracts are subject to renegotiation.
We have sought to minimize the adverse impact from the slower pace of U.S. military orders on our results of operations by seeking to obtain foreign military orders, expanding our customer base as well as seeking new commercial business. We do not expect these markets to completely mitigate the negative impact of lower U.S. defense spending.
If we fail to scale our operations appropriately in response to changes in demand, we may be unable to meet competitive challenges or exploit potential market opportunities, and our business could be materially and adversely affected.
Significant fluctuations in customer demand place a significant strain on our management personnel, infrastructure and resources. To implement our current business and product plans, we need to appropriately manage our cost base, as well as train, manage and motivate our workforce, while continuing to maintain our critical operational and financial systems and our manufacturing and service capabilities. All of these endeavors require substantial management effort and potential capital. If we are unable to effectively manage our operations to our customer demand levels, we may be unable to scale our business quickly enough to meet competitive challenges or exploit potential market opportunities, and our current or future business could be materially and adversely affected.
Low unemployment and tight labor markets may adversely affect our labor costs and our ability to hire and retain a sufficient workforce required to meet the backlog and customer demands. If we are not able to maintain a sufficient workforce and attract and retain additional personnel as required, we may not be able to implement our business plan and our results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
We compete with several other large defense contractors, as well as homebuilding, industrial manufacturing and warehousing industries within the immediate area of our manufacturing facilities for both lower and higher skill level manufacturing employees. The limited supply of available workers for hire, combined with increasing competition among other local industries, may result in increased production costs associated with higher wages, employee bonuses, overtime premiums and enhanced employee benefits in addition to cost increases associated with employee recruitment, employee turnover, training and learning curve inefficiencies. We may be unable to fill the labor positions required to meet our customer demands in a timely or cost-effective manner, which would impede our ability to meet current or increasing production levels in line with our customer expectations and adversely affect our ability to grow revenue or maintain our current margin levels.
| 19 |
Our ability to fulfill our backlog may have an effect on our long-term ability to procure contracts and fulfill current contracts.
Our ability to fulfill our backlog may be limited by our ability obtain material supplies and to devote sufficient financial and human capital resources. Disruptions in our supply chain and transportation delays, combined with inflationary pressures and tight labor market conditions could impede our ability to meet customer requirements. If we do not fulfill our backlog in a timely manner, we may experience delays in product delivery which would postpone receipt of revenue from those delayed deliveries. Additionally, if we are consistently unable to fulfill our backlog, this may be a disincentive to customers to award large contracts to us in the future until they are comfortable that we can effectively manage our backlog.
We do not have employment agreements with our key personnel, other than our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, and our management has minimal unencumbered equity ownership in us. If we are not able to retain our key personnel or attract additional key personnel as required, we may not be able to implement our business plan and our results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
We depend to a large extent on the abilities and continued participation of our executive officers and other key employees. The loss of either executive officer or any other key employee could have a material adverse effect on our business. We currently have only two employment agreements. We presently maintain “key man” insurance on the Chief Executive Officer. We believe that experienced personnel will continue to be required to implement our business plan. Competition for such personnel is intense, and we cannot assure you that they will be available when required, or that we will have the ability to attract and retain them. In addition, due to our small size, we do not presently have depth of staffing in our executive, operational and financial management areas in order to have an effective succession plan should the need arise. Thus, in the event of the loss of one or more of our management employees, our results of operations could be vulnerable to challenges associated with recruiting additional key personnel.
Certain of our products are dependent on specialized sources of supply potentially subject to disruption which could have a material, adverse impact on our business.
We expect recent supply chain disruptions driven by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the related sanctions, combined with raw material shortages, labor shortages, and transportation delays, to continue for the foreseeable future. These conditions have strained our suppliers and extended supplier delivery lead times, affecting their ability to sustain operations. Further, a dockworker strike on the east coast which has been suspended until January 15, 2025, pending negotiations, could have a negative impact on our ability to obtain key manufacturing materials such as adhesives and epoxies should the strike ensue and continue for a sustained period of time beyond our safety stock levels. We have experienced market wide material shortages for paint and resin products as well as critical epoxies and chemicals used in our manufacturing process. In addition, we have seen substantial increases in the costs of aluminum, steel and acrylic commodities and experienced supplier schedule delays for other key components which were driven by supplier labor and material shortages. In several cases, spotty supply and material shortages have resulted in stocking higher inventory “safety stock” levels to ensure adequate lead time to replenish critical supplies.
We have selectively single-sourced some of our material components in order to mitigate excess procurement costs associated with significant tooling and startup costs. Furthermore, because of the nature of government contracts, we are often required to purchase selected items from U.S. government approved suppliers, which may further limit our ability to utilize multiple supply sources for these key components.
To the extent any of these single sourced or government approved suppliers may have disruptions in deliveries due to production, quality, or other issues, we may also experience related production delays or unfavorable cost increases associated with retooling and qualifying alternate suppliers. The impact of delays resulting from disruptions in supply for these items could negatively impact our revenue, our reputation with our customers, and our results of operations. In addition, significant price increases from single-source suppliers could have a negative impact on our profitability to the extent that we are unable to recover these cost increases on our fixed price contracts.
Each contract has a specific quantity of material which needs to be purchased, assembled, and shipped. Prior to bidding on a contract, we contact potential sources of material and receive qualified quotations for this material. In some cases, the entire volume is given to a single supplier and in other cases, the volume might be split between several suppliers. If a contract has a single source supplier and that supplier fails to meet their obligations (e.g., quality, delivery), then we would seek to find an alternate supplier and bring this information back to the final customer. Contractual deliverables would then generally be re-negotiated (e.g., specifications, delivery, price). As of September 29, 2024, approximately 7% of our material requirements were single-sourced across 10 suppliers representing approximately 15% of our active supplier order value. Single-sourced component requirements span across all of our major product lines.
| 20 |
We consider it a material financial or schedule risk if we believe it will take us at least three months to identify and qualify a suitable replacement for specialized single source suppliers. In the table below, we identify those specialized single source suppliers with respect to which we face such a material risk and the product lines supported by those materials utilized by us as of September 29, 2024.
| Product Line | Supply Item | Risk | Purchase Orders | |||
| Sighting Systems DDAN | Digital camera system | Alternative source would take in excess of six months to qualify | Current firm fixed price & quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. | |||
| Periscopes | Die-cast housings | All die cast tooling is consolidated at this supplier. It would take approximately six months to move tooling and re-qualify a new supplier. | Current firm fixed price & quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. Supplier is on schedule. | |||
| Periscopes | Steel castings | Alternative supplier source would take six months to qualify. | Current firm fixed price & quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. | |||
| Vision Blocks | Military Spec welded housings for vision blocks | Would take approximately 8-10 months to re-qualify a new supplier source. | Currently working with current vendor to keep supply of these parts | |||
| Vision Blocks | Large/Small/Customs Blocks | Would take approximately 4-6 months to re-qualify a new supplier source. | Currently working with single source for purchasing material on a forecast projection basis | |||
| MRS | Aluminum Castings for Housing | Would take approximately 8-12 months to re-qualify a new supplier source. | Currently, ordering for a single source, new casting tool and FAT will be required to qualify a new source | |||
| Big Eye | Sand castings for big eye binocular parts | Would take approximately 4-6 months to re-qualify a new supplier source | Current firm fixed price & quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. | |||
| Beamsplitter | Glass tight dimensions and Special Coating | Limited number of suppliers that can meet tight customer specifications without deviation | Current firm fixed price & quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. | |||
Applied Optics Center
M22/M24 Binocular |
Spare Components | Only approved source due to proprietary rights. Alternate source cannot be developed. | Current firm fixed price and quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. Supplier is on schedule. | |||
Applied Optics Center LIF Assembly |
Container Wrench and Retaining Ring | Mold tooling was manufactured by and used by one source. Tooling would not fit other potential supplier’s equipment. Finding another source would be very expensive and take approximately 1 year to transition | Current firm fixed price and quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. Supplier is on schedule. |
| 21 |
Applied Optics Center LIF Assembly |
Rubber Seal | Mold tooling was manufactured by and used by one source. Tooling would not fit other potential supplier’s equipment. Finding another source would be very expensive and take approximately 1 year to transition | Current firm fixed price and quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. Supplier is on schedule. | |||
Applied Optics Center Assorted LFU Assemblies |
Anti-Reflective Device | Only one approved government source of supply at this time | Current firm fixed price and quantity purchase orders are in place with the supplier to meet all contractual requirements. Supplier is on schedule. |
The defense technology supply industry is subject to technological change and if we are not able to keep up with our competitors and/or they develop advanced technology as response to our products, we may be at a competitive disadvantage.
The market for our products is generally characterized by technological developments, evolving industry standards, changes in customer requirements, frequent new product introductions and enhancements, short product life cycles and severe price competition. Our competitors could also develop new, more advanced technologies in reaction to our products. Currently accepted industry standards may change. Our success depends substantially on our ability, on a cost-effective and timely basis, to continue to enhance our existing products and to develop and introduce new products that take advantage of technological advances and adhere to evolving industry standards. An unexpected change in one or more of the technologies related to our products, in market demand for products based on a particular technology or of accepted industry standards could materially and adversely affect our business. We may or may not be able to develop new products in a timely and satisfactory manner to address new industry standards and technological changes, or to respond to new product announcements by others. In addition, new products may or may not achieve market acceptance.
Unexpected warranty and product liability claims could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
The possibility of future product failures could cause us to incur substantial expense to repair or replace defective products. We warrant the quality of our products to meet customer requirements and be free of defects for twelve months subsequent to delivery. We establish reserves for warranty claims based on our historical rate of returned shipments against these contracts. There can be no assurance that this reserve will be sufficient if we were to experience an unexpectedly high incidence of problems with our products. Significant increases in the incidence of such claims may adversely affect our sales and our reputation with consumers. Costs associated with warranty and product liability claims could materially affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We rely on the proper function, availability and security of information technology systems to operate our business and a cyber-attack or other breach of these systems could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
We rely on information technology systems to process, transmit, and store electronic information in our day-to-day operations. Similar to other companies, the size and complexity of our information technology systems makes them vulnerable to a cyber-attack, malicious intrusion, breakdown, destruction, loss of data privacy, or other significant disruption. Our information systems require an ongoing commitment of significant resources to maintain, protect, and enhance existing systems and develop new systems to keep pace with continuing changes in information processing technology, evolving systems and regulatory standards.
On July 13, 2021, we experienced a ransomware attack. While that attack did not have material adverse consequences, similar attacks, if not caught and effectively addressed in a timely manner, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Any failure by us to maintain or protect our information technology systems and data integrity, including from cyber-attacks, intrusions or other breaches, could result in the unauthorized access to personally identifiable information, theft of intellectual property or other misappropriation of assets, or otherwise compromise our confidential or proprietary information and disrupt our operations. Any of these events may cause us to have difficulty preventing, detecting, and controlling fraud, be subject to legal claims and liability, have regulatory sanctions or penalties imposed, have increases in operating expenses, incur expenses or lose revenues as a result of a data privacy breach or theft of intellectual property, or suffer other adverse consequences, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
| 22 |
We derive almost all of our revenue from a small number of customers and the loss of any of these customers could have a material adverse effect on our revenues.
The Company’s revenues for fiscal year ended September 29, 2024 were derived from sales to U.S. government agencies (20%), four major U.S. defense contractors (25%, 7%, 6% and 6%), one major commercial customer (13%) and all other customers (23%). Approximately 94% of total Company revenue is generated from domestic customers and 6% is derived from foreign customers. In particular, a decision by one of our major defense contract customers, U.S. government agencies or other major customers to cease issuing contracts to us could have a significant material impact on our business and results of operations given that they represent over 77% of our gross business revenue. There can be no assurance that we could replace these customers on a timely basis or at all.
We have approximately 150 discrete contracts with major defense contractors, the U.S. Government (primarily Defense Logistics Agencies (DLA)), and other prime U.S. defense contractors. If they choose to terminate these contracts, we are entitled to fully recover all contractual costs and reasonable profits incurred up to or as a result of the terminated contract.
We possess only six patents and rely primarily on trade secrets to protect our intellectual property.
We utilize several highly specialized and unique processes in the manufacture of our products, for which we rely solely on trade secrets to protect our innovations. We cannot assure you that we will be able to maintain the confidentiality of our trade secrets or that our non-disclosure agreements will provide meaningful protection of our trade secrets, know-how or other proprietary information in the event of any unauthorized use, misappropriation or other disclosure. The non-disclosure agreements that are designed to protect our trade secrets could be breached, and we might not have adequate remedies for the breach. It is also possible that our trade secrets will otherwise become known or independently developed by our competitors, many of which have substantially greater resources than us, and these competitors may have applied for or obtained, or may in the future apply for or obtain, patents that will prevent, limit or interfere with our ability to make and sell some of our products. Although based upon our general knowledge (and we have not conducted patent searches), we believe that our products do not infringe on the patents or other proprietary rights of third parties; however, we cannot assure you that third parties will not assert infringement claims against us or that such claims will not be successful.
We may need to raise additional capital in the future beyond any cash flow from our existing business; additional funds may not be available on terms that are acceptable to us, or at all.
We may need to raise additional capital in the future to finance our future working capital needs. We cannot assure you that any additional capital will be available on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all. Future equity or debt financings may be difficult to obtain. If we are not able to obtain additional capital as may be required, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
We anticipate that our capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
| ● | our ability to fulfill backlog; | |
| ● | our ability to procure additional production contracts; | |
| ● | our ability to control costs; | |
| ● | the timing of payments and reimbursements from government and other contracts, including but not limited to changes in federal government military spending and the federal government procurement process; | |
| ● | increased sales and marketing expenses; | |
| ● | technological advancements and competitors’ response to our products; | |
| ● | capital improvements to new and existing facilities; | |
| ● | our relationships with customers and suppliers; and | |
| ● | general economic conditions including the effects of future economic slowdowns, acts of war or terrorism and the current international conflicts. |
| 23 |
Even if available, financings may involve significant costs and expenses, such as legal and accounting fees, diversion of management’s time and efforts, and substantial transaction costs. If adequate funds are not available on acceptable terms, or at all, we may be unable to finance our operations, develop or enhance our products, expand our sales and marketing programs, take advantage of future opportunities or respond to competitive pressures.
Risks Related to our Credit Facility and Liquidity
Our level of debt and restrictions in our credit agreement could negatively affect our operations and limit our liquidity and our ability to react to changes in the economy.
Our Loan Agreement with Texas Capital Bank contains restrictive covenants that require us to maintain a fixed charge coverage ratio of at least 1.25:1 and a total leverage ratio of 3.00:1, which we may fail to meet if there is a material decrease in our profitability or liquidity. In addition, the Loan Agreement contains restrictive covenants governing indebtedness, liens, fundamental changes (including changes in management), investments, and restricted payments (including cash dividends). The borrowings under the Loan Agreement are secured by substantially all of our operating assets as collateral.
A breach of any of the restrictions and covenants could result in a default under our Loan Agreement, which, if not cured or waived, could cause any outstanding indebtedness under the agreement (or under any future financing arrangements) to become immediately due and payable, and result in the termination of commitments to extend further credit. We may not have sufficient funds on hand to repay the loan, and if we are forced to refinance these borrowings on less favorable terms, or are unable to refinance at all, our results of operations and financial condition could be materially adversely affected by increased costs and rates.
If our debt level significantly increases in the future, it could have significant consequences on our ongoing operations including requiring us to dedicate a significant portion of our cash flow from operations to servicing debt rather than using it to execute our strategic initiatives; limiting our ability to obtain additional debt financing for future working capital, capital expenditures, or other worthwhile endeavors; and limiting our ability to react to changes in the market.
Risks Related to Our Stock
Our stock typically trades in low volumes daily which could lead to illiquidity, volatility, or depressed stock price.
Our stock is listed on Nasdaq, but typically trades in low daily volumes. Because of a history of low trading volume, our stock is relatively illiquid and its price may be volatile. This may make it more difficult for our stockholders to resell shares when desired or at attractive prices. Some investors view low-volume stocks as unduly speculative and therefore not appropriate candidates for investment. Also, due to the low volume of shares traded on any trading day, persons buying or selling in relatively small quantities may easily influence prices of our stock.
Any analysts covering our stock could negatively impact the stock price.
The trading market for our common stock will likely be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts may publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors. If any such analysts downgrade their evaluation of our stock, the price of our stock could decline. Furthermore, if our operating results fail to meet analysts’ expectations, our stock price would likely decline.
Our stock price has been and will likely continue to be extremely volatile, and, as a result, stockholders may not be able to resell shares at or above their purchase price, and we may be more vulnerable to securities class action litigation.
Since our common stock was listed on Nasdaq in March 2023, our stock price, as reported by Nasdaq, has ranged from a low of $2.87 to a high of $10.30. As a result, the market price and trading volume of our common stock is likely to be similarly volatile in the future, and investors in our common stock may experience a decrease, which could be substantial, in the value of their stock, including decreases unrelated to our results of operations or prospects, and could lose part or all of their investment.
In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been brought against that company. Because of the potential volatility of our stock price, we may become the target of securities litigation in the future. If we were to become involved in securities litigation, it could result in substantial costs, divert management’s attention and resources from our business and adversely affect our business.
| 24 |
We are a “smaller reporting company” as defined in SEC regulations, and the reduced disclosure requirements applicable to smaller reporting companies may make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are a “smaller reporting company” as defined under SEC regulations and we may, and do, take advantage of certain exemptions from reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not smaller reporting companies including, among other things, reduced financial disclosure requirements including being permitted to provide only two years of audited financial statements and reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation. As a result, our stockholders may not have access to certain information that they may deem important. We could remain a smaller reporting company indefinitely. As a smaller reporting company, investors may deem our stock less attractive and, as a result, there may be less active trading of our common stock, and our stock price may be more volatile.
General Risk Factors
Changes in current economic conditions may adversely affect our ability to continue operations.
Changes in current economic conditions may cause a decline in business, consumer and defense spending and capital market performance, which could adversely affect our business and financial performance. Our ability to raise funds, which could be required for business continuity or expansion of our operations, may be adversely affected by current and future economic conditions, such as a reduction in the availability of credit, financial market volatility and economic recession.
In the future, we may look to acquire other businesses in our industry and the acquisitions will require us to use substantial resources.
In the future, we may decide to pursue acquisitions of other businesses in our industry. In order to successfully acquire other businesses, we would be forced to spend significant resources for both acquisition and transactional costs, which could divert substantial resources in terms of both financial and personnel capital from our current operations. Additionally, we might assume liabilities of the acquired business, and the repayment of those liabilities could have a material adverse impact on our cash flow. Furthermore, when a new business is integrated into our ongoing business, it is possible that there would be a period of integration and adjustment required which could divert resources from ongoing business operations.
The elimination of monetary liability against our directors, officers and employees under Delaware law and the existence of indemnification rights to our directors, officers and employees may result in substantial expenditures by us and may discourage lawsuits against our directors, officers and employees.
We provide indemnification to our directors and officers to the extent provided by Delaware law. The foregoing indemnification obligation could result in our incurring substantial expenditures to cover the cost of settlement or damage awards against directors and officers, which we may be unable to recoup. These provisions and resultant costs may also discourage us from bringing a lawsuit against directors and officers for breaches of their fiduciary duties and may similarly discourage the filing of derivative litigation by our stockholders against our directors and officers even though such actions, if successful, might otherwise benefit us and our stockholders.
Our stock price is speculative, and there is a risk of litigation.
The trading price of our common stock has in the past and may in the future be subject to wide fluctuations in response to factors such as the following:
| ● | revenue or results of operations in any quarter failing to meet the expectations, published or otherwise, of the investment community; | |
| ● | speculation in the press or investment community; | |
| ● | wide fluctuations in stock prices, particularly with respect to the stock prices for other defense industry companies; | |
| ● | announcements of technological innovations by us or our competitors; | |
| ● | new products or the acquisition of significant customers by us or our competitors; | |
| ● | changes in investors’ beliefs as to the appropriate price-earnings ratios for us and our competitors; | |
| ● | changes in management; | |
| ● | sales of common stock by directors and executive officers; | |
| ● | rumors or dissemination of false or misleading information, particularly through Internet chat rooms, instant messaging, and other rapid-dissemination methods; | |
| ● | conditions and trends in the defense industry generally; | |
| ● | the announcement of acquisitions or other significant transactions by us or our competitors; | |
| ● | adoption of new accounting standards affecting our industry; | |
| ● | general market conditions; | |
| ● | domestic or international terrorism and other factors; and | |
| ● | other factors as described in this section. |
| 25 |
Fluctuations in the price of our common stock may expose us to the risk of securities class action lawsuits. Although no such lawsuits are currently pending against us and we are not aware that any such lawsuit is threatened to be filed in the future, there is no assurance that we will not be sued based on fluctuations in the price of our common stock. Defending against such suits could result in substantial cost and divert management’s attention and resources. In addition, any settlement or adverse determination of such lawsuits could subject us to significant liability.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Strategy
We recognize the increasing volume and sophistication of cyber threats and take our responsibility to protect the information and systems under our purview seriously. We consider cybersecurity threat risks alongside other Company risks as part of our overall risk assessment process. Our cybersecurity processes aim to provide a comprehensive approach to assess, identify, manage, mitigate, and respond to cybersecurity threats.
We maintain a cybersecurity risk program predicated on a risk-based approach. We use cost-effective controls that are commensurate with the risk and sensitivity of our specific information systems, control systems and enterprise data. Our cybersecurity program incorporates best practices and industry standards from multiple sources and is designed to comply with applicable regulations. The cybersecurity program includes, but is not limited to, the following elements: risk assessment, policies and procedures, training and awareness, auditing, log collection and analysis, threat hunting and intelligence surveillance, compliance monitoring and testing, and incident response.
Our internal professionals collaborate with external subject matter specialists, as necessary. All third parties engaged for such matters are subjected to scrutiny to ensure they satisfy our security standards. We periodically review our third-party engagements to ensure that the providers maintain the necessary levels of protection and competency, as well as to oversee and identify potential cybersecurity risks and/or threats from such engagements.
We describe how risks from cybersecurity threats could materially affect us, including our business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition, as part of our risk factor disclosures at Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Cybersecurity Governance
Cybersecurity is an important part of our risk management processes and an area of focus for our Board and management. Our Board is responsible for oversight of our cybersecurity risk, including the effectiveness of cybersecurity risk management policies and protocols, while our Facilities Security Officer (“FSO”), and IT Manager are responsible for assessing and managing cybersecurity risk. We use a third-party service which monitors the Company’s security threats twenty-four hours each day throughout the year. Any detected deviation from the expected operating parameters will initiate a communication to our IT Manager for investigation and remediation of the detected deviation in a timely manner.
Our IT Manager provides timely reports on cyber security incidents to the FSO, Danny Schoening, who also serves as the CEO and as Chairman of the board of directors. These reports may in turn be presented to the full board depending on the severity of the incident. In the event of a major incident, the Company’s Incident Response policy will be executed and the appropriate parties notified.
Item 2. Properties
We are headquartered in Richardson, TX and lease approximately 93,967 combined square feet of facilities between Richardson, Texas and Dallas, Texas. We operate with a single shift, and capacity could be expanded by adding a second shift.
We renewed the lease on our 49,100 square foot, Richardson, Texas facility, effective as of January 11, 2021, for eighty-six (86) months, commencing on April 1, 2021 and ending on May 31, 2028. Our Applied Optics Center, is located in Dallas, Texas with leased premises consisting of approximately 44,867 square feet of space. The Applied Optics Center lease was renewed on January 11, 2021 for eighty-six (86) months, commencing on November 1, 2021 and ending on December 31, 2028. The Applied Optics Center amendment provides for a five-year renewal option at the end of the lease term at the greater of the then “prevailing rental rate” or the then current base rent rate.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
From time to time, we are involved in lawsuits, claims, investigations and proceedings, including pending opposition proceedings involving patents that arise in the ordinary course of business. There are no matters pending that we expect to have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
None.
| 26 |
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market information
Our common stock is listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “OPXS”.
On December 18, 2024, the closing price for our common stock was $8.91 per share.
Securities outstanding and holders of record
On December 18, 2024, there were approximately 87 shareholders of record for our common stock and 6,896,738 shares of our common stock issued and outstanding.
Dividends
We have in the past paid dividends but we have no plans to do so in the foreseeable future.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
There were no purchases made by or on behalf of the Company or any “affiliated purchaser” (as defined in Rule 10b-18(a)(3) of its common stock under the Exchange Act) during the three months ended September 29, 2024.
Item 6. Reserved
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and the related notes that are set forth in our financial statements elsewhere in this Annual Report.
This management’s discussion and analysis reflects information known to management as of our fiscal year end, September 29, 2024, and the date of filing. This MD&A is intended to supplement and complement our audited financial statements and notes thereto for the year ended September 29, 2024, prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). You are encouraged to read our financial statements in conjunction with this MD&A. The financial information in this MD&A has been prepared in accordance with GAAP, unless otherwise indicated. In addition, we use non-GAAP financial measures as supplemental indicators of our operating performance and financial position. We use these non-GAAP financial measures internally for comparing actual results from one period to another, as well as for planning purposes. We will also report non-GAAP financial results as supplemental information, as we believe their use provides more insight into our performance. When a non-GAAP measure is used in this MD&A, it is clearly identified as a non-GAAP measures and reconciled to the most closely corresponding GAAP measure.
The following discussion highlights the principal factors that have affected our financial condition and results of operations as well as our liquidity and capital resources for the periods described. This discussion contains forward-looking statements. Please see “Special cautionary statement concerning forward-looking statements” and “Risk factors” for a discussion of the uncertainties, risks and assumptions associated with these forward-looking statements. The operating results for the periods presented were not significantly affected by inflation.
All references in the following section to 2023 or 2024 with respect to our financial position and results of operations are to our fiscal years ended October 1, 2023 or September 29, 2024, respectively.
Background
Optex Systems, Inc. manufactures optical sighting systems and assemblies for the U.S. Department of Defense, foreign military applications and commercial markets. Its products are installed on a variety of U.S. military land vehicles, such as the Abrams and Bradley fighting vehicles, light armored and advanced security vehicles and the Stryker family of vehicles. Optex Systems, Inc. (Delaware) also manufactures and delivers numerous periscope configurations, rifle and surveillance sights and night vision optical assemblies. Optex Systems, Inc. (Delaware) products consist primarily of build-to-customer print products that are delivered both directly to the armed services and to other defense prime contractors. Less than 1% of our revenue is related to the resale of products substantially manufactured by others. In this case, the product would likely be a simple replacement part of a larger system previously produced by Optex Systems, Inc. (Delaware).
We are both a prime and sub-prime contractor to the Department of Defense. Sub-prime contracts are typically issued through major defense contractors such as General Dynamics Land Systems, Raytheon Corp., BAE, ADS Inc. and others. We are also a military supplier to foreign governments such as Israel, Australia and the NATO Support and Procurement Agency and South American countries, and as a subcontractor for several large U.S. defense companies serving foreign governments.
| 27 |
By way of background, the Federal Acquisition Regulation (“FAR”) is the principal set of regulations that govern the acquisition process of government agencies and contracts with the U.S. government. In general, parts of the FAR are incorporated into government solicitations and contracts by reference as terms and conditions effecting contract awards and pricing solicitations.
Many of our contracts are prime or subcontracted directly with the Federal government and, as such, are subject to FAR Subpart 49.5, “Contract Termination Clauses” and more specifically Federal Acquisition Regulation clauses 52.249-2 “Termination for Convenience of the Government Fixed-Price)”, and 49.504 “Termination of fixed-price contracts for default”. These clauses are standard clauses on our prime military contracts and generally apply to us as subcontractors. It has been our experience that the termination for convenience is rarely invoked, except where it is mutually beneficial for both parties. We are currently not aware of any material pending terminations for convenience or for default on our existing contracts.
In the event a termination for convenience were to occur, FAR clause 52.249-2 provides for full recovery of all contractual costs and profits reasonably occurred up to and as a result of the terminated contract. In the event a termination for default were to occur, we could be liable for any excess cost incurred by the government to acquire supplies from another supplier similar to those terminated from us. We would not be liable for any excess costs if the failure to perform the contract arises from causes beyond the control and without the fault or negligence of the Company as defined by FAR clause 52.249-8.
In addition, some of our contracts allow for government contract financing in the form of contract progress payments pursuant to FAR 52.232-16, “Progress Payments”. Subject to certain limitations, this clause provides for government payment of up to 90% of incurred program costs prior to product delivery for small businesses like us. To the extent our contracts allow for progress payments, we intend to utilize this benefit, thereby minimizing the working capital impact on Optex Systems Holdings for materials and labor required to complete the contracts.
Material Trends and Recent Developments
We have experienced substantial increases in the costs of aluminum, steel and acrylic commodities, which has affected our net income in the year ended September 29, 2024 and is expected to continue to have a negative effect on the margins generated under several of our long-term fixed contracts over the next two years. See also “Item 1A. Risk Factors – Risks Related to Our Business - Certain of our products are dependent on specialized sources of supply potentially subject to disruption which could have a material, adverse impact on our business.”
We have experienced significant material shortages during the fiscal year ended October 1, 2023 and the first half of fiscal year ended September 29, 2024 from several significant suppliers of our periscope covers and housings. These shortages affect several of our periscope products at the Optex Richardson segment. The delays in key components, combined with labor shortages during the first half of the fiscal year ended September 29, 2024, have negatively impacted our production levels and have pushed back expected delivery dates. We have obtained an alternative source for one of our key components and are expediting our other suppliers to support the increased production levels.
We have seen improvements in the local labor market since 2023 and increased our direct labor force and employee overtime in concert with improvements in our supplier delivery performance. Further, we have invested in additional machinery and equipment and other process improvements to increase production capacity and alleviate process bottlenecks. While we are encouraged by improvements in supplier performance and available manpower for the Optex Richardson segment periscope line which yielded increased revenue performance during fiscal year 2024, we have yet to ramp up deliveries sufficiently to keep pace with our current customer demands. As such, we cannot give any assurances that expected customer delivery dates for our periscope products will not experience further delays.
We refer also to “Item 1. Business – Market Opportunity: U.S. Military” for a description of current trends in U.S. government military spending and its potential impact on Optex, which may be material, including particularly the tables included in that section and disclosure on the significant reduction in spending for U.S ground system military programs, which has a direct impact on the Optex Systems Richardson segment revenue, all of which is incorporated herein by reference.
We
refer to “Item 1. Business – Recent Events” of this report for recent developments affecting the Company.
| 28 |
Results of Operations by Segment
We have presented the operating results by segment to provide investors with an additional tool to evaluate our operating results. Management of Optex Systems Holdings uses the selected financial measures by segment internally to evaluate its ongoing segment operations and to allocate resources within the organization accordingly. Segments are determined based on differences in products, location, internal reporting and how operational decisions are made. Management has determined that the Optex Systems, Richardson plant (to which we refer below as the Optex Systems segment or Optex Systems), and the Applied Optics Center, Dallas plant, which was acquired on November 3, 2014 (to which we refer below as the Applied Optics Center segment or Applied Optics Center), are separately managed, organized, and internally reported as separate business segments. The table below provides a summary of selective statement of operations data by operating segment for the years ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023 reconciled to the Audited Consolidated Results of Operations as presented in Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data”.
Results of Operations Selective Financial Info
(Thousands)
| Twelve months ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Optex Systems Richardson | Applied Dallas | Other (non- | Consolidated | Optex Systems Richardson | Applied
Optics Dallas | Other (non- | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue from External Customers | $ | 18,171 | $ | 15,824 | $ | - | $ | 33,995 | $ | 12,120 | $ | 13,539 | $ | - | $ | 25,659 | ||||||||||||||||
| Intersegment Revenues | - | 1,042 | (1,042 | ) | - | - | 893 | (893 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Segment Revenue | 18,171 | 16,866 | (1,042 | ) | 33,995 | 12,120 | 14,432 | (893 | ) | 25,659 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Cost of Sales | 14,401 | 11,107 | (1,042 | ) | 24,466 | 9,729 | 10,204 | (893 | ) | 19,040 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Profit | 3,770 | 5,759 | - | 9,529 | 2,391 | 4,228 | - | 6,619 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Margin % | 20.7 | % | 34.1 | % | - | 28.0 | % | 19.7 | % | 29.3 | % | - | 25.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| General and Administrative Expense | 3,630 | 653 | 425 | 4,708 | 3,121 | 464 | 247 | 3,832 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Segment Allocated G&A Expense | (1,486 | ) | 1,486 | - | - | (1,338 | ) | 1,338 | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net General & Administrative Expense | 2,144 | 2,139 | 425 | 4,708 | 1,783 | 1,802 | 247 | 3,832 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) | 1,626 | 3,620 | (425 | ) | 4,821 | 608 | 2,426 | (247 | ) | 2,787 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) % | 8.9 | % | 21.5 | % | - | 14.2 | % | 5.0 | % | 16.8 | % | - | 10.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Expense | - | - | (47 | ) | (47 | ) | - | - | (55 | ) | (55 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Income (Loss) before taxes | $ | 1,626 | 3,620 | (472 | ) | 4,774 | $ | 608 | 2,426 | (302 | ) | 2,732 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) before taxes % | 8.9 | % | 21.5 | % | - | 14.0 | % | 5.0 | % | 16.8 | % | - | 10.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Our total external sales revenues increased by $8.3 million in the fiscal year 2024, or 32.5% compared to the 2023 fiscal year. The Optex Systems segment realized a $6.1 million, or 49.9% increase, and the Applied Optics Center segment realized an increase of $2.3 million, or 16.9%, in external revenue compared to the prior year period. Intersegment revenues were $1.0 million for 2024 and $0.9 million in 2023. Intersegment revenues relate primarily to coated filters provided by the Applied Optics Center to Optex Systems in support of the Optex Systems periscope line.
| 29 |
Gross profit increased $2.9 million and the gross margin percentage increased by 2.2 points from 25.8% in the 2023 fiscal year to 28.0% in the 2024 fiscal year. Optex Systems gross profit increased by $1.4 million and the gross margin percentage increased to 20.7% as compared to 19.7% in the prior year period. Applied Optics Center gross profit increased by $1.5 million and the gross margin percentage increased to 34.1% as compared to 29.3% in the prior year period. The increase in each segment and consolidated gross profit is primarily attributable to higher revenue and increased absorption of fixed cost.
Consolidated general and administrative costs increased from $3.8 million for the twelve months ended October 1, 2023 to $4.7 million for the twelve months ended September 29, 2024. General and administrative costs increased $0.9 million due to increased royalties and selling expenses of $0.4 million, increased stock compensation expenses of $0.2 million, increased labor and fringe costs of $0.2 million and increased information technology costs of $0.1 million. During the fiscal years 2024 and 2023, Applied Optics Center absorbed $1.5 million and $1.3 million, respectively, of fixed general and administrative costs incurred by Optex Systems for support services. The increase in allocated general and administrative expenses during the 2024 year is directly attributable to increased general and administrative costs during the current year period as compared to the prior year. These expenses cover accounting, executive, human resources, information technology, board fees and other corporate expenses paid by Optex Systems and shared across both operating segments.
Consolidated operating income increased by $2.0 million in the year ended September 29, 2024 to $4.8 million as compared to the prior year operating income of $2.8 million. The increase in operating income is primarily attributable to higher revenue and gross profit, partially offset by increases in general and administrative costs. The operating income increased across both segments as compared to the prior year on higher revenue and gross profit.
Income before taxes increased $2.0 million, to $4.8 million in the 2024 fiscal year from a prior year income before taxes of $2.7 million. The increase in income before taxes year over year is primarily due to higher revenue and gross profit, partially offset by increased general and administrative costs.
New Orders and Backlog
Product backlog represents the value of unfulfilled customer manufacturing orders yet to be recognized as revenue. While backlog is not a non-GAAP financial measure, it is also not defined by GAAP. Therefore, our methodology for calculating backlog may not be consistent with methodologies used by other companies. The booked backlog by period may also not be fully indicative of the predicted revenues for those periods as many of our orders provide for accelerated delivery without penalty and may additionally provide customers the option to adjust schedules to meet their most recent projected demand quantities. However, we provide customer order and backlog information as we believe it provides significant insight into forward demand, with some predictive power to short term future revenues.
During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, the Company booked $36.4 million in new orders, representing a 5.2% increase from the prior year period orders of $34.6 million. The orders for the most recently completed twelve months consist of $23.5 million for our Optex Richardson segment and $12.9 million attributable to the Applied Optics Center segment.
The following table depicts the new customer orders for the twelve months ending September 29, 2024 as compared to the prior year period in millions of dollars:
| (Millions) | ||||||||||||||||
| Product Line | Twelve
months September
29, | Twelve months October
1, | Variance | % Chg | ||||||||||||
| Periscopes | $ | 19.9 | $ | 15.9 | $ | 4.0 | 25.2 | |||||||||
| Sighting Systems | 0.4 | 4.0 | (3.6 | ) | (90.0 | ) | ||||||||||
| Howitzer | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Other | 3.2 | 3.4 | (0.2 | ) | (5.9 | ) | ||||||||||
| Optex Systems – Richardson | 23.5 | 23.3 | 0.2 | 0.9 | ||||||||||||
| Optical Assemblies | 1.8 | 1.9 | (0.1 | ) | (5.3 | ) | ||||||||||
| Laser Filters | 9.2 | 7.6 | 1.6 | 21.1 | ||||||||||||
| Day Windows | 0.1 | 0.3 | (0.2 | ) | (66.7 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other | 1.8 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 20.0 | ||||||||||||
| Applied Optics Center – Dallas | 12.9 | 11.3 | 1.6 | 14.2 | ||||||||||||
| Total Customer Orders | $ | 36.4 | $ | 34.6 | $ | 1.8 | 5.2 | |||||||||
| 30 |
During the year ended September 29, 2024, orders in the Company’s Optex Richardson segment increased by $0.2 million, or 0.9%, as compared to the prior year. The primary reason for the increase relates to a prior year award for $3.4 million in sighting systems to repair and refurbish night vision equipment for the Government of Israel. We began shipments against the contract in December 2023. The decrease in orders for sighting systems and other products was offset by a significant increase in periscope orders in the year ended September 29, 2024. The Applied Optics Center orders increased $1.6 million, or 14.2%, as we continue to see increases in orders for laser filter units for several prime government contractors, in addition to an increase in customer orders for other products driven by our new program of Infrared (IR) Signature Reduction Coatings used on aircraft.
The Optex Richardson segment currently has five open US Government IDIQ type military contracts for periscopes, collimators, and big eye assemblies with unspent funding which covers base year and option year requirement ordering periods into January 2029. During the year, approximately 20% of Optex Richardson’s segment orders, or $4.8 million, were awards against active IDIQ contracts. The Applied Optics Center has two open US Government IDIQ orders. During the year, approximately 22% of Applied Optics Center segment orders, or $2.8 million, were awards against active IDIQ contracts. We anticipate additional orders throughout the next five years for these ongoing contracts. In addition, the Company has several open bid requests for new multi-year IDIQ contracts pending with the U.S. Government and other prime contractors for additional periscopes, and unity mirrors that are expected to be awarded in the next three to six months.
Backlog as of September 29, 2024 was $44.2 million as compared to a backlog of $41.8 million as of October 1, 2023, representing an increase of 5.7%. The following table depicts the current expected delivery by quarter of all contracts awarded as of September 29, 2024, as well as the September 29, 2024 backlog as compared to the backlog on October 1, 2023.
(Millions)
| Product Line | Q1 2025 | Q2 2025 | Q3 2025 | Q4 2025 | 2025 Delivery | 2026+ Delivery | Total 9/29/2024 | Total 10/1/2023 | Variance | % Chg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periscopes | $ | 3.6 | $ | 5.7 | $ | 5.6 | $ | 4.7 | $ | 19.6 | $ | 3.1 | $ | 22.7 | $ | 14.9 | $ | 7.8 | 52.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sighting Systems | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 4.7 | (0.9 | ) | (19.1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Howitzer | - | - | - | - | - | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | - | 1.8 | 1.2 | 3.0 | 4.6 | (1.6 | ) | (34.8 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Optex Systems – Richardson | 4.4 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 5.1 | 22.9 | 8.9 | 31.8 | 26.5 | 5.3 | 20.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Optical Assemblies | 0.5 | 0.2 | - | - | 0.7 | - | 0.7 | 2.8 | (2.1 | ) | (75.0 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Laser Filters | 3.3 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 8.7 | 0.8 | 9.5 | 9.9 | (0.4 | ) | (4.0 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Day Windows | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 1.7 | (0.6 | ) | (35.3 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 1.1 | - | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 22.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applied Optics Center – Dallas | 4.4 | 3.3 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 11.3 | 1.1 | 12.4 | 15.3 | (2.9 | ) | (19.0 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Backlog | $ | 8.8 | $ | 9.9 | $ | 9.0 | $ | 6.5 | $ | 34.2 | $ | 10.0 | $ | 44.2 | $ | 41.8 | $ | 2.4 | 5.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Optex Systems - Richardson
During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, backlog for our Optex Richardson segment increased by 20.0%, or $5.3 million to $31.8 million, as compared to the prior year ending backlog of $26.5 million.
Backlog for our periscope product line has increased 52.3% or $7.8 million to $22.7 million, from our 2023 fiscal year end level of $14.9 million, primarily on increased orders above our delivery capacity during the 2024 year. With the majority of material shortages behind us, we have substantially increased the headcount and overtime hours in addition to the purchase of machinery and equipment to eliminate process bottlenecks and increase periscope throughput up to 60-75% over the next year in line with our customer demands. We are anticipating an increase of approximately 60% in periscope revenue in fiscal year 2025 as compared to 2024.
Sighting Systems product line backlog decreased 19.1%, or $0.9 million, to $3.8 million, from our 2023 fiscal year end level of $4.7 million. The decreased backlog is primarily driven by deliveries of $0.7 million against our 2023 order for sighting systems to repair and refurbish night vision equipment for the Government of Israel combined with revenues of $0.2 million recognized against our long term OWSS maintenance contract.
The Howitzer contract awarded in July 2020 continues to experience customer driven delays related to customer furnished materials. This program is currently on hold pending statement of work changes and materials furnished by the customer. We anticipate deliveries against the Howitzer contract to begin in fiscal year 2026.
| 31 |
Our backlog in other product groups decreased by $1.6 million or 34.8% from $4.6 million in 2023 to $3.0 million in 2024 on shipments against a long-term collimator IDIQ of $1.3 million and commercial wedge assemblies of $0.3 million.
Applied Optics Center – Dallas
The Applied Optics Center backlog decreased by $2.9 million, or 19.0%, for the year ended September 29, 2024, from $15.3 million in 2023 to $12.4 million in 2024.
Backlog for our optical assemblies decreased by $2.1 million, or 75.0%, as compared to the prior year on lower customer demand. We anticipate new orders during the next three to six months for deliveries in 2025.
Laser filter backlog decreased by $0.4 million, or 4.0%, during the year due to increased shipments against our laser interface filter and laser filter units during the year. We are anticipating additional orders for shipment during the 2025 year.
Day window backlog decreased by $0.6 million, or 35.3%, during the period as compared to the prior year primarily due to shipments against a long-term IDIQ contract with deliveries scheduled into 2026. We anticipate additional orders in the next three months.
Other Applied Optics backlog increased by $0.2 million, or 22.2% for the year ended September 29, 2024, on an increase in customer orders for Infrared (IR) Signature Reduction Coatings used on aircraft.
Please refer to “Material Trends and Recent Events” above or “Liquidity and Capital Resources” below for more information on recent developments and trends with respect to our orders and backlog, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
The Company continues to pursue domestic, international and commercial opportunities in addition to maintaining its current footprint with U.S. vehicle manufactures, with existing as well as new product lines. We are also reviewing potential products outside our traditional product lines. Further, we continue to look for strategic businesses to acquire that will strengthen our existing product line, expand our operations, offer operational scale and enter new markets.
Twelve months ended September 29, 2024 compared to the twelve months ended October 1, 2023
Revenues
The table below details the revenue changes by segment and product line for the year ended September 29, 2024 as compared to the year ended October 1, 2023.
Twelve months ended
(Millions)
| Product Line | September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | Variance | % Chg | ||||||||||||
| Periscopes | $ | 12.1 | $ | 8.6 | $ | 3.5 | 40.7 | |||||||||
| Sighting Systems | 1.4 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 40.0 | ||||||||||||
| Howitzers | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Other | 4.7 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 88.0 | ||||||||||||
| Optex Systems – Richardson | 18.2 | 12.1 | 6.1 | 50.4 | ||||||||||||
| Optical Assemblies | 3.9 | 5.6 | (1.7 | ) | (30.4 | ) | ||||||||||
| Laser Filters | 9.6 | 6.4 | 3.2 | 50.0 | ||||||||||||
| Day Windows | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 16.7 | ||||||||||||
| Other | 1.6 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 60.0 | ||||||||||||
| Applied Optics Center – Dallas | 15.8 | 13.6 | 2.2 | 16.2 | ||||||||||||
| Total Revenue | $ | 34.0 | $ | 25.7 | $ | 8.3 | 32.3 | |||||||||
Our total revenues increased by $8.3 million, or 32.3% in fiscal year 2024 compared to fiscal year 2023. The Optex Systems Richardson segment realized a $6.1 million, or 50.4%, increase in revenue and the Applied Optics Center segment realized an increase of $2.2 million, or 16.2%, in revenue compared to the prior year.
| 32 |
Optex Systems - Richardson
Revenues on our periscope line increased $3.5 million, or 40.7%, during the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023 on increased customer demand and higher production throughput during the year.
Revenues on sighting systems increased by $0.4 million, or 40.0% from the prior year period due to deliveries against the 2023 order for repair and refurbishment of night vision equipment to the Government of Israel.
Optex Systems-Richardson revenue on other product lines increased by $2.2 million, or 88.0%, compared to revenues in the prior year due to increased orders for collimators, windows, beamsplitters, cell assemblies and other spares.
Applied Optics Center - Dallas
Revenue on optical assemblies decreased by $1.7 million, or 30.4%, during the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 as compared to the prior twelve-month period on lower customer demand. We are anticipating revenue over the next twelve months to approximate the 2024 revenue level pending new customer orders in the next three to six months.
Laser filter revenue increased by $3.2 million, or 50.0%, during the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 as compared to the prior twelve-month period on increased customer demand. We anticipate revenue to continue at the higher levels throughout 2025.
Revenues on our day windows increased by $0.1 million, or 16.7%, during the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 as compared to October 1, 2023 as we continue to ship against the long-term IDIQ contract for these units. We anticipate revenues to continue at this, or a slightly increased, level through 2025.
Applied Optics Center revenue for other product lines increased by $0.6 million, or 60.0%, during the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 as compared to the prior twelve-month period on increased deliveries in products for Infrared (IR) Signature Reduction Coatings used on aircraft. We anticipate these delivery levels to continue into 2025 combined with additional increases for shipments against our current binocular contract.
Gross Margin. The gross margin for the year ended September 29, 2024 was 28.0% of revenue as compared to a gross margin of 25.8% of revenue for the year ended October 1, 2023. Cost of sales increased by $5.4 million to $24.5 million for 2024 compared to $19.0 million for 2023. The gross profit increased by $2.9 million to $9.5 million in 2024 as compared to $6.6 million in 2023. The increase is primarily due to increased revenue, and higher absorption of fixed cost and changes in product mix between the segments.
G&A Expenses. For the years ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, we recorded operating expenses of $4.7 million and $3.8 million, respectively. General and administrative cost increased $0.9 million, or 22.9%, for fiscal year 2024 as compared to the prior year due to increased royalties and selling expenses of $0.4 million, increased stock compensation expenses of $0.2 million, increased labor and fringe costs of $0.2 million and increased information technology costs of $0.1 million. The selling expenses are directly related to new products including the Speedtracker acquisition and the Government of Israel repair and refurbishment on night vision products and the royalties are related to the new Infrared (IR) Signature Reduction Coatings product.
Operating Income. For the year ended September 29, 2024, we recorded operating income of $4.8 million as compared to operating income of $2.8 million during the year ended October 1, 2023. The $2.0 million increase in operating income is primarily due to increased revenue and gross profit, offset by higher general and administrative costs.
Net income applicable to common shareholders. During the year ended September 29, 2024, we recorded net income applicable to common shareholders of $3.8 million as compared to net income applicable to common shareholders of $2.3 million during the year ended October 1, 2023. The increase of net income of $1.5 million is primarily attributable to increased revenue and gross profit, offset by higher general and administrative costs and increased federal income taxes of $0.5 million.
| 33 |
Non GAAP Adjusted EBITDA
We use adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) as an additional measure for evaluating the performance of our business as “net income” includes the significant impact of noncash compensation expenses related to equity stock issues, as well as depreciation, amortization, interest expenses and federal income taxes. We believe that Adjusted EBITDA is a meaningful indicator of our operating performance because it permits period-over-period comparisons of our ongoing core operations before the excluded items, which we do not consider relevant to our operations. Adjusted EBITDA is a financial measure not required by, or presented in accordance with, U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”).
Adjusted EBITDA has limitations and should not be considered in isolation or a substitute for performance measures calculated under GAAP. This non-GAAP measure excludes certain cash expenses that we are obligated to make. In addition, other companies in our industry may calculate Adjusted EBITDA differently than we do or may not calculate it at all, which limits the usefulness of Adjusted EBITDA as a comparative measure.
The table below summarizes our twelve-month operating results for the periods ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, in terms of both the GAAP net income measure and the non-GAAP Adjusted EBITDA measure.
(Thousands) Twelve months ended | ||||||||
| September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | |||||||
| Net Income — GAAP | $ | 3,768 | $ | 2,263 | ||||
| Add: | ||||||||
| Federal Income Tax Expense | 1,006 | 469 | ||||||
| Depreciation & Amortization | 487 | 345 | ||||||
| Stock Compensation | 425 | 247 | ||||||
| Interest Expense | 47 | 55 | ||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA - Non GAAP | $ | 5,733 | $ | 3,379 | ||||
Our Adjusted EBITDA increased by $2.4 million to $5.7 million during the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 as compared to $3.4 million during the twelve months ended October 1, 2023. The increase in EBITDA is primarily driven by increased net income, offset by increased taxes, depreciation and amortization, and stock compensation. Operating segment performance is discussed in greater detail throughout the previous sections.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of September 29, 2024, Optex Systems Holdings had working capital of $15.1 million, as compared to $13.5 million as of October 1, 2023. During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, we generated operating cash of $1.8 million, primarily driven by increased revenue and net income. As of September 29, 2024, there was no net change against the outstanding credit facility balance of $1.0 million.
The Company has capital commitments of $0.3 million for the purchase of property and equipment consisting of a significant coating chamber upgrade, a black bond dispensing machine, an air compressor, and an Opotek tunable laser system.
Backlog as of September 29, 2024 was $44.2 million as compared to a backlog of $41.8 million as of October 1, 2023, representing an increase of 5.7%. For further details, see “Results of Operations – New Orders and Backlog” above.
The Company has historically funded its operations through cash from operations, convertible notes, common and preferred stock offerings and bank debt. The Company’s ability to generate positive cash flows depends on a variety of factors, including the continued development and successful marketing of the Company’s products.
At September 29, 2024, the Company had approximately $1.0 million in cash and an outstanding payable balance of $1.0 against its $3.0 million line of credit. As of September 29, 2024, our outstanding accounts receivable balance was $3.8 million, which has been collected during the first quarter of fiscal 2025. During the first quarter of 2025, we paid down our credit facility to zero.
We refer to the disclosure above under “Material Trends and Recent Developments” with respect to recent supply chain disruptions and material shortages, which disclosure is incorporated herein by reference.
| 34 |
In the short term, the Company plans to utilize its current cash, available line of credit and operating cash flow to fund inventory purchases in support of the backlog growth and higher anticipated revenue during the next twelve months. Short term cash in excess of our working capital needs may be also be used to fund the purchase of product lines and other assets. We may also repurchase common stock against our current stock repurchase plan. Longer term, excess cash beyond our operating needs may be used to fund new product development, company, product line or other asset acquisitions, or additional stock purchases as attractive opportunities present themselves.
On January 18, 2024, the Company acquired certain intellectual property and technical and marketing information relating to the Speedtracker Mach product line and entered into an asset purchase agreement and a contract manufacturing agreement with RUB Aluminium s.r.o. (“RUB”). The Company acquired the assets using $1 million cash on hand, with potential additional future cash payments based on successful completion of defined milestones. The initial term of the contract manufacturing agreement is one year, subject to additional one-year renewal terms. After the acquisition, the Company determined it would be more economical to move the manufacturing operations in house and is no longer ordering assembled units under the original contract manufacturing agreement. RUB will continue to provide the Company with purchased kit parts for the manufacture of the Speedtracker Mach products.
The acquisition included transaction costs of $30 thousand for legal fees. Pursuant to the asset purchase agreement, the total earnout payment will be $238 thousand only if the earnout revenue milestone is achieved during the earnout period, otherwise the earnout will be zero. As of September 29, 2024, it was determined that the earnout revenue milestone was unlikely to be achieved during the earnout period and the fair value of the contingent liability was zero. The asset will be amortized on a straight-line basis over a seven-year period.
In some instances, new contract awards may allow for government contract financing in the form of contract progress payments pursuant to FAR 52.232-16, “Progress Payments.” Subject to certain limitations, this clause provides for government payment of up to 90% of incurred program costs prior to product delivery for small businesses like us. To the extent any contracts allow for progress payments and the respective contracts would result in significant preproduction cash requirements for design, process development, tooling, material or other resources which could exceed our current working capital or line of credit availability, we intend to utilize this benefit to minimize any potential negative impact on working capital prior to receipt of payment for the associated contract deliveries. Currently none of our existing contracts allow for progress payments.
We refer to “Note 8 – Commitments and Contingencies – Rental Payments under Non-cancellable Operating Leases” for a tabular depiction of our remaining minimum lease and estimated Common Area Maintenance (“CAM”) payments under such leases as of September 29, 2024, which disclosure is incorporated herein by reference.
The Company expects to generate net income and positive cash flow from operating activities over the next twelve months. To remain profitable, we need to maintain a level of revenue adequate to support our cost structure. Management intends to manage operations commensurate with its level of working capital and line of credit facility during the next twelve months and beyond; however, uneven revenue levels driven by changes in customer delivery demands, first article inspection requirements or other program delays associated with the pandemic could create a working capital shortfall. In the event the Company does not successfully implement its ultimate business plan, certain assets may not be recoverable.
On March 22, 2023, the Company and its subsidiary, Optex Systems, Inc. (“Optex”, and with the Company, the “Borrowers”), entered into a Business Loan Agreement (the “Loan Agreement”) with Texas Capital Bank (the “Lender”), pursuant to which the Lender will make available to the Borrowers a revolving line of credit in the principal amount of $3 million (the “Credit Facility”). The commitment period for advances under the Credit Facility is twenty-six months expiring on May 22, 2025. We refer to the expiration of that time period as the “Maturity Date.” Outstanding advances under the Credit Facility will accrue interest at a rate equal to the secured overnight financing rate (SOFR) plus a specified margin, subject to a specified floor interest rate. The interest rate is currently at 7.509% per annum. As of September 29, 2024, the interest rate was 7.67% per annum.
The Loan Agreement contains customary events of default (including a 25% change in ownership) and negative covenants, including but not limited to those governing indebtedness, liens, fundamental changes (including changes in management), investments, and restricted payments (including cash dividends). The Loan Agreement also requires the Borrowers to maintain a fixed charge coverage ratio of at least 1.25:1 and a total leverage ratio of 3.00:1. The Credit Facility is secured by substantially all of the operating assets of the Borrowers as collateral. The Borrowers’ obligations under the Credit Facility are subject to acceleration upon the occurrence of an event of default as defined in the Loan Agreement. The Loan Agreement further provides for a $125,000 Letter of Credit sublimit. As of September 29, 2024, there was $1.0 million borrowed under the Credit Facility. As of September 29, 2024, the Company was in compliance with all covenants under the Credit Facility.
The Credit Facility replaced the prior $2 million line of credit with PNC Bank, National Association.
| 35 |
On September 22, 2021 the Company announced authorization for an additional $1 million stock repurchase program. As of September 29, 2024, there was an authorized balance of $560 thousand remaining to be spent against the repurchase program. During the years ended September 29,2024 and October 1, 2023, there were no stock repurchases against the plan.
During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 the Company declared and paid no dividends. As of September 29, 2024, there are no outstanding declared and unpaid dividends.
Critical Accounting Estimates
A critical accounting estimate is an estimate that:
| ● | is made in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, | |
| ● | involves a significant level of estimation uncertainty, and | |
| ● | has had or is reasonably likely to have a material impact on the company’s financial condition or results of operation. |
Our significant accounting policies are fundamental to understanding our results of operations and financial condition. Some accounting policies require that we use estimates and assumptions that may affect the value of our assets or liabilities and financial results. These policies are described in Note 2 “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” of Item 8 “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this report.
Our critical accounting estimates include warranty costs, contract losses and the deferred tax asset valuation. Future warranty costs are based on the estimated cost of replacement for expected returns based upon our most recent experience rate of defects as a percentage of warranty covered sales. Our warranty covered sales primarily include the Applied Optics Center optical assemblies. While our warranty period is 12 months, our reserve balances assume a general 90-day return period for optical assemblies previously delivered plus any returned backlog in-house that has not yet been repaired or replaced to our customer. If our actual warranty returns should significantly exceed our historical rates on new customer products, significant production changes, or substantial customer changes to the 90-day turn-around times on returned goods, the impact could be material to our operating profit. We have not experienced any significant changes to our warranty trends in the preceding three years and do not anticipate any significant impacts in the near term. We monitor the actual warranty costs incurred to the expected values on a quarterly basis and adjust our estimates accordingly. As of September 29, 2024, the Company had accrued warranty costs of $52 thousand, as compared to $75 thousand as of October 1, 2023. The primary reason for the decrease in reserve balances relates to lower shipments of our optical assemblies during the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 as compared to the prior year.
As of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, we had $259 thousand, and $243 thousand, respectively, of contract loss reserves included in our balance sheet accrued expenses. These loss contracts are related to some of our older legacy periscope IDIQ contracts which were priced in 2018 through early 2020, prior to Covid-19 and the subsequent decline in revenue at the Optex Systems Richardson segment combined with significant inflationary pressures on materials and labor in the last two years. Due to inflationary price increases on component parts and higher internal manufacturing costs (as a result of escalating labor costs and higher burden rates), some of these contracts are in a loss condition, or at marginal profit rates. These contracts are typically three-year IDIQ contracts with two optional award years, and as such, we are obligated to accept new task awards against these contracts until the contract expiration. Should contract costs continue to increase above the negotiated selling price, or in the event the customer should release substantial quantities against these existing loss contracts, the losses could be material. For contracts currently in a loss status based on the estimated per unit contract costs, losses are booked immediately on new task order awards. During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, the accrued contract losses increased by $16 thousand on new awards against one of our loss IDIQ contracts, partially offset by shipments during the twelve month period. There is no way to reasonably estimate future inflationary impacts, or customer awards on the existing loss contracts. We continue to monitor these contracts throughout the year for any significant changes in addition to seeking potential cost saving strategies to mitigate risk.
As of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, Optex Systems Inc. had a net carrying value of $0.9 million in deferred tax assets consisting of deferred tax assets of $1.7 million and valuation reserves of ($0.8) million. The valuation allowance covers certain deferred tax assets where we believe we will be unlikely to recover those tax assets through future operations. The valuation reserve includes assumptions related to future taxable income which would be available to cover net operating loss carryforward amounts. Because of the uncertainties of future income forecasts combined with the complexity of some of the deferred assets, these forecasts are subject to change over time. While we believe our current estimate to be reasonable, changing market conditions and profitability, changes in equity structure and changes in tax regulations may impact our estimated reserves in future periods.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Recent Accounting Pronouncements are detailed under Note 3 of Item 8 “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this report.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Not applicable.
| 36 |
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
Optex Systems Holdings, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the entity’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
Critical audit matters are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. We determined that there are no critical audit matters.
/s/
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2017.
December 19, 2024
| 37 |
Optex Systems Holdings, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| (Thousands, except share and per share data) | ||||||||
| September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | $ | ||||||
| Accounts Receivable, Net | ||||||||
| Inventory, Net | ||||||||
| Contract Asset | ||||||||
| Prepaid Expenses | ||||||||
| Current Assets | ||||||||
| Property and Equipment, Net | ||||||||
| Other Assets | ||||||||
| Deferred Tax Asset | ||||||||
| Intangibles, net | ||||||||
| Right-of-use Asset | ||||||||
| Security Deposits | ||||||||
| Other Assets | ||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | $ | ||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities | ||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $ | $ | ||||||
| Credit Facility | ||||||||
| Operating Lease Liability | ||||||||
| Federal Income Taxes Payable | ||||||||
| Accrued Expenses | ||||||||
| Accrued Selling Expense | ||||||||
| Accrued Warranty Costs | ||||||||
| Contract Loss Reserves | ||||||||
| Customer Advance Deposits | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities | ||||||||
| Other Liabilities | ||||||||
| Credit Facility-Long Term | ||||||||
| Operating Lease Liability, net of current portion | ||||||||
| Other Liabilities | ||||||||
| Total Liabilities | ||||||||
| Commitments and Contingencies | ||||||||
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||||
| Common Stock – ($par, authorized, and shares issued and outstanding, respectively) | ||||||||
| Additional Paid in Capital | ||||||||
| Accumulated Deficit | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $ | $ | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| 38 |
Optex Systems Holdings, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Income
| (Thousands, except share and per share data) | ||||||||
| Twelve months ended | ||||||||
| September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | $ | ||||||
| Cost of Sales | ||||||||
| Gross Profit | ||||||||
| General and Administrative Expense | ||||||||
| Operating Income | ||||||||
| Interest Expense | ||||||||
| Income Before Taxes | ||||||||
| Income Tax Expense, net | ||||||||
| Net income applicable to common shareholders | $ | $ | ||||||
| Basic income per share | $ | $ | ||||||
| Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding - basic | ||||||||
| Diluted income per share | $ | $ | ||||||
| Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding - diluted | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| 39 |
Optex Systems Holdings, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| (Thousands) | ||||||||
| Twelve months ended | ||||||||
| September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | |||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | ||||||||
| Net Income | $ | $ | ||||||
| Adjustments to Reconcile Net Income to Net Cash provided by (used in) Operating Activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | ||||||||
| Stock Compensation Expense | ||||||||
| Change in Deferred Tax Asset | ( | ) | ||||||
| Accounts Receivable | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Bad Debt Expense | ||||||||
| Inventory | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Contract Asset | ( | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid Expenses | ||||||||
| Leases | ||||||||
| Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses | ||||||||
| Federal Income Taxes Payable | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accrued Warranty Costs | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accrued Selling Expense | ( | ) | ||||||
| Customer Advance Deposits | ( | ) | ||||||
| Increase (Decrease) In Accrued Estimated Loss On Contracts | ( | ) | ||||||
| Total Adjustments | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net Cash provided by (used in) Operating Activities | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash Flows used in Investing Activities | ||||||||
| Purchases of Intangible Assets | ( | ) | ||||||
| Purchases of Property and Equipment | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net Cash used in Investing Activities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Cash Flows (used in) provided by Financing Activities | ||||||||
| Cash Paid for Taxes Withheld On Net Settled Restricted Stock Unit Share Issue | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Borrowings from Credit Facility | ||||||||
| Payments to Credit Facility | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net Cash (used in) provided by Financing Activities | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net (Decrease) Increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Year | ||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Year | $ | $ | ||||||
| Supplemental Cash Flow Information: | ||||||||
| Cash Transactions: | ||||||||
| Cash Paid for Taxes | ||||||||
| Cash Paid for Interest | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| 40 |
Optex Systems Holdings, Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
| Thousands (except share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Common | Additional | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Common | Paid in | Accumulated | Stockholders | ||||||||||||||||
| Issued | Stock | Capital | Deficit | Equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at October 2, 2022 | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||||||
| Stock Compensation Expense | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Vested restricted stock units issued net of tax withholding | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Shares Issued(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited Unvested Shares(2) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at October 1, 2023 | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||||||
| Stock Compensation Expense | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Vested restricted stock units issued net of tax withholding | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at September 29, 2024 | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | |
| (2) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| 41 |
Note 1 — Organization and Operations
Optex
Systems Holdings, Inc. (“the Company”) manufactures optical sighting systems and assemblies for the U.S. Department of Defense,
foreign military applications and commercial markets. Its products are installed on a variety of U.S. military land vehicles, such as
the Abrams and Bradley fighting vehicles, light armored and advanced security vehicles, and have been selected for installation on the
Stryker family of vehicles. Optex Systems Holdings also manufactures and delivers numerous periscope configurations, rifle and surveillance
sights and night vision optical assemblies. Optex Systems Holdings’ products consist primarily of build to customer print products
that are delivered both directly to the military and to other defense prime contractors or commercial customers. Optex Systems Holdings’
operations are based in Dallas and Richardson, Texas in leased facilities comprising
Note 2 — Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
Principles of Consolidation: The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Optex Systems Holdings and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Optex Systems, Inc. All significant inter-company balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates: The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statement and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from the estimates.
Segment Reporting: FASB ASC 280 requires that a public business enterprise report financial and descriptive information about its reportable operating segments. Operating segments are components of an enterprise about which separate financial information is available and evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker in decisions regarding resource allocations and performance assessments. Generally, financial information is required to be reported on the basis that it is used internally for evaluating segment performance and deciding how to allocate resources to segments. Segments are determined based on differences in products, internal reporting and how operational decisions are made. Management has determined that the Optex Systems, Richardson plant, and the Applied Optics Center, Dallas plant are separately managed, organized, and internally reported as separate business segments. The FASB ASC 280 requires that a public business enterprise report a measure of segment profit or loss, certain specific revenue and expense items, and segment assets. It requires reconciliations of total segment revenues, total segment profit or loss, total segment assets, and other amounts disclosed for segments to corresponding amounts in the enterprise’s general-purpose financial statements.
Fiscal Year: Optex System Holdings’ fiscal year ends on the Sunday nearest September 30. Fiscal year 2024 ended on September 29, 2024 and included 52 weeks. Fiscal year 2023 ended on October 1, 2023 and included 52 weeks.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments: Fair value estimates discussed herein are based upon certain market assumptions and pertinent information available to management as of the financial statement presentation date.
The carrying value of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued liabilities, are carried at, or approximate, fair value as of the reporting date because of their short-term nature. The credit facility is reported at fair value as it bears market rates of interest.
The fair value hierarchy prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value and requires that assets and liabilities carried at fair value be classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
Level 1: Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Observable market-based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data.
Level 3: Unobservable inputs reflecting the reporting entity’s own assumptions.
| 42 |
The accounting guidance establishes a hierarchy which requires an entity to maximize the use of quoted market prices and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. An asset or liability’s level is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Fair value estimates are reviewed at the origination date and again at each applicable measurement date and interim or annual financial reporting dates, as applicable for the financial instrument, and are based upon certain market assumptions and pertinent information available to management at those times.
Cash
and Cash Equivalents: For financial statement presentation purposes, Optex Systems Holdings considers those short-term, highly
liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less to be cash or cash equivalents. Optex Systems Holdings has $
Concentration
of Credit Risk: The Company’s revenues for fiscal year ended September 29, 2024 were derived from sales to U.S. government
agencies (
Accounts
Receivable: Optex Systems Holdings records its accounts receivable at the original sales invoice amount less
liquidations for previously collected advance/progress bills and an allowance for expected credit losses. As of the fiscal year
beginning October 2, 2023, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2016-13, “Financial Instruments –
Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments.” Under the new standard, the current
expected credit loss (“CECL”) model is used for estimating an allowance for credit losses and an allowance is set up
when the receivable is initially recorded, even if the probability of loss is remote. The Company utilizes a CECL model based on the
aging schedule method. As the customer base is primarily U.S. government and government prime contractors, Optex Systems Holdings
allowance for credit losses is minimal. On a quarterly basis, Optex Systems Holdings evaluates its accounts receivable and
establishes an allowance for credit losses, using a CECL model based on a rolling aging schedule method. An account receivable is considered to be past due if any portion of the receivable balance is outstanding beyond
its scheduled due date. No interest is accrued on past due accounts receivable. As of September
29, 2024, and October 1, 2023, Optex Systems Holdings had an allowance for credit losses of $
As
of September 29, 2024,
Inventory: Inventory is recorded at the lower of cost or net realizable value and adjusted as appropriate for decreases in valuation and obsolescence. Adjustments to the valuation and obsolescence reserves are made after analyzing market conditions, current and projected sales activity, inventory costs and inventory balances to determine appropriate reserve levels. Cost is determined using the first-in first-out method. As of September 29, 2024, and October 1, 2023 inventory included:
| (Thousands) | ||||||||
As of September 29, 2024 | As of October 1, 2023 | |||||||
| Raw Materials | $ | $ | ||||||
| Work in Process | ||||||||
| Finished Goods | ||||||||
| Gross Inventory | ||||||||
| Less: Inventory Reserves | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net Inventory | $ | $ | ||||||
In
the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 Optex Systems recorded $
| 43 |
Warranty
Costs: Some of Optex Systems Holdings’ customers require that the Company warrant the quality of its products to meet customer
requirements and be free of defects for up to twelve months subsequent to delivery. Future warranty costs are based on the estimated
cost of replacement for expected returns based upon our most recent experience rate of defects as a percentage of warranty covered sales.
Throughout the year, warranty costs are expensed as incurred, and as of each year end, Optex Systems Holdings reviews the prior 12-month
warranty experience rate and may adjust the warranty accrual as required to cover any estimated warranty expenses associated with the
period end backlog of returned customer units awaiting repair or replacement plus any estimated warranty expenses related to anticipated
future returns on previous deliveries. As of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, the existing warranty reserve balances of $
The table below summarizes the warranty expenses and incurred warranty costs for the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023.
| Years ended | ||||||||
| 2024 | 2023 | |||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | $ | ||||||
| Incurred costs for warranties satisfied during the period | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Warranty Expenses: | ||||||||
| Warranties reserved for new product shipped during the period(1) | ||||||||
| Change in estimate for pre-existing warranty liabilities (2) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Warranty Expense | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | $ | ||||||
| (1) | ||
| (2) |
Property
and Equipment: Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the
estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from to
Leases: In February 2016, FASB issued ASU 2016-02—Leases (Topic 842). The update is intended to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. As such, Optex Systems Holdings adopted these provisions as of the fiscal year beginning on September 30, 2019. Optex Systems Holdings has two significant operating facilities leases which extend beyond twelve months and fall under the guidance of ASC Topic 842. See also Note 8.
Revenue
Recognition: The Company has adopted FASB ASC 606—Revenue from Contracts with Customers which requires revenue recognition
based on a five-step model that includes: identifying the contract, identifying the performance obligations, determining the transaction
price, allocating the transaction price and recognizing the revenue. The standard results in the recognition of revenue depicting the
transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount reflecting the expected consideration to be received from the customer
for such goods and services, based on the satisfaction of performance obligations, occurring when the control of the goods or services
transfer to the customer. The majority of the Company’s contracts and customer orders originate with fixed determinable unit prices
for each deliverable quantity of goods defined by the customer order line item (performance obligation) and include the specific due
date for the transfer of control and title of each of those deliverables to the customer at pre-established payment terms, which are
generally within thirty to sixty days from the transfer of title and control. We have elected to account for shipping and handling costs
as fulfillment costs after the customer obtains control of the goods. In addition, the Company has one ongoing service contract which
relates to optimized weapon system support (OWSS) and includes ongoing program maintenance, repairs and spare inventory support for the
customer’s existing fleet units in service during the duration of the contract. Revenue recognition for this program has been recorded
by the Company, and compensated by the customer, at fixed monthly increments over time, consistent with the defined contract maintenance
period. The total revenue recognized over time related to the contract is $
| 44 |
The Company has on occasion, outside of the presented periods, received selective contract awards and modifications which included substantive milestone performance obligations, contract modifications, negotiated settlements and financing arrangements which could fall within the scope of FASB ASC 606 revenue recognition guidance on reoccurrence, and as such, the Company has expanded their contract review process to ensure any new contract awards, changes, modifications, financing arrangements or potential negotiated settlements are recorded in compliance to the new standard guidance.
During
the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, there was $
As
of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, there was $
Customer
Advance Deposits: Customer advance deposits represent amounts collected from customers in advance of shipment or revenue recognition
which relate to undelivered product due to non-substantive milestone payments or other cash in advance payment terms. As of September
29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, Optex Systems, Inc. had a balance of $
Contract
Loss Reserves: The Company records loss provisions in the event that the current estimated total revenue against a contract and
the total estimated cost remaining to fulfill the contract indicate a loss upon completion. When the estimated costs indicate a loss,
we record the entire value of the loss against the contract loss reserve in the period the determination is made. The Company has several
long-term fixed price contracts that are currently indicative of a loss condition due to recent inflationary pressures on material and
labor, combined with increased manufacturing overhead costs. As of September 29, 2024, the Company had contract loss reserves of $
Government Contracts: Many of Optex Systems Holdings’ contracts are prime or subcontracted directly with the Federal government and as such, are subject to FAR Subpart 49.5, “Contract Termination Clauses” and more specifically FAR 52.249-2 “Termination for Convenience of the Government (Fixed-Price)”, and FAR 49.504 “Termination of fixed-price contracts for default”. These clauses are standard clauses on prime military contracts and are required by the government to be “flowed down” by the prime contractor to any subcontractors used to perform work or provide components against the award. It has been Optex Systems Holdings’ experience that the termination for convenience is rarely invoked, except where it has been mutually beneficial for both parties. Optex Systems Holdings is not currently aware of any pending terminations for convenience or default on its existing prime contracts or customer purchase orders.
Impairment
or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets: Optex Systems Holdings follows the provisions of FASB ASC 360-10, “Accounting for
the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets”. This standard requires, among other things, that long-lived assets be reviewed
for potential impairment whenever events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts may not be recoverable. The assessment of
possible impairment is based on the ability to recover the carrying value of the asset from the expected future pre-tax cash flows (undiscounted
and without interest charges) of the related operations. If these cash flows are less than the carrying value of such assets, an impairment
loss is recognized for the difference between estimated fair value and carrying value. The measurement of impairment requires management
to estimate future cash flows and the fair value of long-lived assets. The Company reviewed the intangible assets as of September 29,
2024 and found
| 45 |
Income Tax/Deferred Tax: FASB ASC 740 requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differing treatment of items for financial reporting and income tax reporting purposes. The deferred tax balances are adjusted to reflect tax rates by tax jurisdiction, based on currently enacted tax laws, which will be in effect in the years in which the temporary differences are expected to reverse. Under FASB ASC 740, the effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. A valuation allowance is provided for certain deferred tax assets if it is more likely than not that Optex Systems Holdings will not realize tax assets through future operations. When assessing the recoverability of deferred tax assets, management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies and results of recent operations. Based on those estimates, management has determined that a portion of the deferred tax assets may not be realized and has established a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset balance. We record uncertain tax positions in accordance with ASC 740 on the basis of a two-step process in which (1) we determine whether it is more likely than not that the tax positions will be sustained on the basis of the technical merits of the position and (2) for those tax positions that meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold, we recognize the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely to be realized upon ultimate settlement with the related tax authority.
As
of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, Optex Systems Inc. has a net carrying value of $
The potentially dilutive securities that Optex Systems Holdings had outstanding were restricted shares, restricted stock units and performance-based shares. Optex Systems Holdings uses the Treasury Stock Method to compute the dilutive effect of these securities. Securities that are anti-dilutive are excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per common share.
For the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, unvested restricted stock units and unvested restricted shares (which converts to incremental dilutive shares) were included in the diluted earnings per share calculation as dilutive. For the twelve months ended October 1, 2023, unvested restricted stock units, restricted unvested shares and performance shares (which converts to incremental dilutive shares) were included in the diluted earnings per share calculation as dilutive and performance shares were excluded from diluted earnings per share as they were below the target share price.
Note 3 — Recent Accounting Pronouncements
There are no significant recent accounting pronouncements that affect the Company.
Note 4 — Segment Reporting
The Company’s reportable segments are strategic businesses offering similar products to similar markets and customers; however, the companies are operated and managed separately due to differences in manufacturing technology, equipment, geographic location, and specific product mix. Applied Optics Center was acquired as a unit, and the management at the time of the acquisition was retained. Both the Applied Optics Center and Optex Systems – Richardson operate as reportable segments under the Optex Systems, Inc. corporate umbrella. For both segments, the chief operating decision maker is Danny Schoening, CEO.
The Applied Optics Center segment also serves as the key supplier of laser coated filters used in the production of periscope assemblies for the Optex Systems-Richardson (“Optex Systems”) segment. Intersegment sales and transfers are accounted for at annually agreed to pricing rates based on estimated segment product cost, which includes segment direct manufacturing and general and administrative costs, but exclude profits that would apply to third party external customers.
| 46 |
Optex Systems (OPX) – Richardson, Texas
Optex
Systems revenues are primarily in support of prime and subcontracted military customers. Approximately
Optex
Systems is located in Richardson Texas, with leased premises consisting of approximately
Applied Optics Center (AOC) – Dallas, Texas
The
Applied Optics Center serves primarily domestic U.S. customers. Sales to commercial customers represent
The
Applied Optics Center is located in Dallas, Texas with leased premises consisting of approximately
The financial table below presents the information for each of the reportable segments profit or loss as well as segment assets for each year. The Company does not allocate interest expense, income taxes or unusual items to segments.
Reportable Segment Financial Information (thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Twelve months ended September 29, 2024 | ||||||||||||||||
Optex Systems Richardson | Applied Optics Center Dallas | Other (non-allocated | Consolidated Total | |||||||||||||
| Revenues from external customers | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Intersegment revenues | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Total Revenue | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Income (loss) before taxes | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||
| Other significant noncash items: | ||||||||||||||||
| Allocated home office expense | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Warranty expense | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Segment Assets | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Expenditures for segment assets | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| 47 |
Reportable Segment Financial Information (thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Twelve months ended October 1, 2023 | ||||||||||||||||
Optex Systems Richardson | Applied Optics Center Dallas | Other (non-allocated | Consolidated Total | |||||||||||||
| Revenues from external customers | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Intersegment revenues | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Total Revenue | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Income (loss) before taxes | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||
| Other significant noncash items: | ||||||||||||||||
| Allocated home office expense | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Warranty expense | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Segment Assets | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Expenditures for segment assets | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
Note 5 — Property and Equipment
A summary of property and equipment at September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023 is as follows:
| (Thousands) | ||||||||||
Estimated Useful Life | September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | ||||||||
| Property and Equipment | ||||||||||
| Furniture and Fixtures | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Machinery and Equipment | ||||||||||
| Leasehold Improvements | ||||||||||
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net Property & Equipment | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Depreciation Expense | $ | $ | ||||||||
During
the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, Optex Systems Holdings purchased $
Note 6 – Asset Purchase of Intellectual Property
On
January 18, 2024, Optex Systems Holdings, Inc., through its wholly-owned subsidiary Optex Systems, Inc. (collectively, the “Company”),
entered into an asset purchase agreement and a contract manufacturing agreement with RUB Aluminum s.r.o. (“RUB”). Under the
agreements, the Company acquired certain intellectual property and technical and marketing information relating to the Speedtracker Mach
product line, which is primarily used for firearm projectile speed detection, measuring and tracking. RUB may continue to manufacture
Speedtracker Mach products on behalf of the Company. The Company acquired the assets using $
| 48 |
During
the twelve months ending September 29, 2024, the Company invested an additional $
The
intangible assets are reviewed annually at each fiscal year end for possible impairment. The Company reviewed intangible assets as of
September 29, 2024 and found
As of September 29, 2024 the value of intangible assets is:
| September 29, 2024 | ||||
| Intangible Assets – Intellectual Property Acquisition | $ | |||
| Software App Development | ||||
| Amortization of Intangible Assets | ( | ) | ||
| Net Intangible Assets | $ | |||
Note 7 — Accrued Expenses
The components of accrued liabilities as of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023 are summarized below:
| (Thousands) | ||||||||
| September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | |||||||
| Accrued Vacation | $ | $ | ||||||
| Property Taxes | ||||||||
| Operating Expenses | ||||||||
| Payroll & Payroll Related | ||||||||
| Total Accrued Expenses | $ | $ | ||||||
Note 8 — Commitments and Contingencies
Rental Payments under Non-cancellable Operating Leases
Optex Systems Holdings leases its office and manufacturing facilities for the Optex Systems, Inc. Richardson location and the Applied Optics Center Dallas location. The Company also leases certain office equipment under non-cancellable operating leases.
The
leased facility under Optex Systems Inc. located at 1420 Presidential Drive, Richardson, Texas consists of
| 49 |
The
leased facility under the Applied Optics Center located at 9839 and 9827 Chartwell Drive, Dallas, Texas, consists of
As of September 29, 2024, the remaining minimum base lease and estimated common area maintenance (CAM) payments under the non-cancellable office equipment and facility space leases are as follows:
Non-cancellable Operating Leases Minimum Payments
| (Thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Optex Richardson | Applied Optics Center | Office Equipment | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal Year | Facility Lease Payments | Facility Lease Payments | Lease Payments | Total Lease Payments | Total Variable CAM Estimate | |||||||||||||||
| 2025 Base year lease | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||
| 2026 Base year lease | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2027 Base year lease | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2028 Base year lease | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2029 Base year lease | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total base lease payments | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||
| Imputed interest on lease payments (1) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total Operating Lease Liability(2) | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||
| Right-of-use Asset(3) | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||
| (1) | |
| (2) | |
| (3) |
Total
expense under both facility lease agreements as of the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 was $
Total
office equipment rentals included in operating expenses was $
Note 9 — Debt Financing
Credit Facility — PNC Bank (formerly BBVA, USA)
On April 16, 2020, Optex Systems Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiary, Optex Systems, Inc. (collectively, the “Borrowers”) entered into a line of credit facility (the “PNC Facility”) with BBVA, USA. In June 2021, PNC Bank completed its acquisition of BBVA, USA and the bank name changed to PNC Bank (“PNC”). The substantive terms were as follows:
| ● | The
principal amount of the PNC Facility was $ |
| 50 |
| ● | ||
| ● | The
PNC Facility contained commercially standard events of default including, but not limited to, not making payments when due; incurring
a judgment of $ | |
| ● | The PNC Facility was secured by a first lien on all of the assets of Borrower. |
On
April 12, 2022, the Borrowers entered into an Amended and Restated Loan Agreement (the “PNC Loan Agreement”) with PNC, pursuant
to which the Borrowers’ existing revolving line of credit facility was decreased from $
On
November 21, 2022, the Borrowers issued an Amended and Restated Revolving Line of Credit Note (the “Line of Credit Note”)
to PNC in connection with an increase of the Borrowers’ revolving line of credit facility under the Loan Agreement from $
The Line of Credit Note and PNC Loan Agreement contained customary events of default and negative covenants, including but not limited to those governing indebtedness, liens, fundamental changes, investments, and restricted payments. The PNC Facility was secured by substantially all of the operating assets of the Borrowers as collateral. The Borrowers’ obligations under the credit facility were subject to acceleration upon the occurrence of an event of default as defined in the Line of Credit Note and PNC Loan Agreement.
The PNC Facility was replaced by the Texas Capital Facility on March 22, 2023.
Credit Facility — Texas Capital Bank
On
March 22, 2023, the Borrowers entered into a Business Loan Agreement (the “Loan Agreement”) with Texas Capital Bank (the
“Lender”), pursuant to which the Lender will make available to the Borrowers a revolving line of credit in the principal
amount of $
The
commitment period for advances under the Texas Capital Facility is twenty-six months expiring on
The
Loan Agreement contains customary events of default (including a
The
outstanding balance under the Texas Capital Facility was $
| 51 |
For
the year ended September 29, 2024, the total interest expense under the Texas Capital Facility was $
Restricted Stock, Performance Shares and Restricted Stock Units issued to Directors, Officers and Employees
The following table summarizes the status of Optex Systems Holdings’ aggregate non-vested restricted stock and restricted stock units, and performance shares:
| Restricted Stock Units | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | Restricted Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | Performance Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding at October 2, 2022 | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Granted | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vested | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding at October 1, 2023 | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Granted | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vested | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding at September 29, 2024 | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
On January 2, 2019, the Company granted and restricted stock units with a January 2, 2019 grant date to Danny Schoening and Karen Hawkins, respectively, vesting as of January 1 each year subsequent to the grant date over a period at a rate of % in year one, and % each year thereafter. The stock price at grant date was $ per share. Effective December 1, 2021, the vesting terms of Danny Schoening’s Restricted Stock Unit (RSU) grant from January 2019 were revised as described below. The Company amortizes the grant date fair value of $ thousand to stock compensation expense on a straight-line basis across the vesting period beginning on January 2, 2019. As of September 29, 2024, there was unrecognized compensation cost relating to this award.
On February 17, 2020, the Company granted restricted stock units to Bill Bates, General Manager of the Applied Optics Center. The restricted stock units vest as of January 1 each year subsequent to the grant date over a period at a rate of % in year one, and % each year thereafter. The stock price at grant date was $ per share. The Company amortized the grant date fair value of $ thousand to stock compensation expense on a straight-line basis across the vesting period beginning on February 17, 2020.
On April 30, 2020, the Board of Directors voted to increase the annual board compensation for the three independent directors from $to $with The total fair value for the shares was $ thousand based on the stock price of $ as of April 30, 2020. On each of January 1, 2021, January 1, 2022, and January 1, 2023, of the restricted director shares vested. On February 16, 2023, of the unvested restricted shares were forfeited and cancelled when one of the independent directors departed the Board. On May 9, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a grant of shares of restricted stock to independent board member Dayton Judd. The shares vest % on each of January 1, 2024 and January 1, 2025. As of the grant date, the fair value of the shares was $ thousand, to be amortized on a straight-line basis through December 31, 2024. The Company amortizes the grant date fair value to stock compensation expense on a straight-line basis across the -year and -year vesting periods beginning on April 30, 2020 and May 9, 2023, respectively. As of September 29, 2024 there were unvested restricted shares outstanding.
| 52 |
The Company entered into an amended and restated employment agreement with Danny Schoening dated December 1, 2021.The updated employment agreement also served to amend Mr. Schoening’s RSU Agreement, dated January 2, 2019, by changing the third and final vesting date for the restricted stock units granted under such agreement from January 1, 2022 to the “change of control date,” that being the first of the following to occur with respect to the Company: (i) any “Person,” as that term is defined in Sections 13(d) and 14(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), with certain exclusions, is or becomes the “Beneficial Owner” (as that term is defined in Rule 13d-3 under the Exchange Act), directly or indirectly, of securities of the Company representing fifty percent (50%) or more of the combined voting power of the Company’s then outstanding securities; or (ii) the Company is merged or consolidated with any other corporation or other entity, other than: (A) a merger or consolidation which would result in the voting securities of the Company outstanding immediately prior thereto continuing to represent (either by remaining outstanding or by being converted into voting securities of the surviving entity) more than fifty percent (50%) of the combined voting power of the voting securities of the Company or such surviving entity outstanding immediately after such merger or consolidation; or (B) the Company engages in a merger or consolidation effected to implement a recapitalization of the Company (or similar transaction) in which no “Person” (as defined above) acquires fifty percent (50%) or more of the combined voting power of the Company’s then outstanding securities. The amended RSU Agreement contained certain exceptions to the definition of change of control.
As of the December 1, 2021 modification date related to the third and final vesting date of the unvested restricted stock units held by Danny Schoening, there was no change in the fair value of the modified award as compared to the original award immediately prior to the modification date. The restricted stock units initially were certain to vest on January 1, 2022, but due to the modification, they were less certain to vest, contingent on a “change in control” occurring, which change in control, in case Mr. Schoening was terminated by the Company without cause or he resigns with good reason prior to such change in control, was required to occur prior to March 13, 2023. As of the modification date, there was $ thousand of unrecognized compensation cost associated with the original award. As a matter of expediency, the unrecognized compensation expense as of the modification date was fully expensed through January 1, 2022. There is no additional compensation expense associated with the modification of the restricted stock unit agreement.
On November 28, 2022, the Company entered into a new employment agreement with Danny Schoening which amended Mr. Schoening’s RSU Agreement, dated January 2, 2019, which had been previously amended as of December 1, 2021, by changing the third and final vesting date for the restricted stock units granted under such agreement from the “change of control date” to January 1, 2023.
On
January 4, 2023, the Company issued common shares to Danny Schoening, CEO, and Bill Bates (AOC GM), net of tax withholding of
$
On
May 1, 2023, the Company granted an aggregate of restricted stock units to eleven employees under
its 2023 Equity Incentive Plan. As of the grant date, assuming a
On May 3, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a grant of and performance shares to Danny Schoening, CEO, and Karen Hawkins, CFO, respectively. Each performance share represents a contingent right to receive one share of common stock. The performance shares vest in five equal increments if, in each case and during a . The fair value of the shares, as of the grant date, was $ thousand based on the derived service periods using a Monte Carlo simulation valuation model. The fair value was amortized through May 17, 2024 when all of the shares had fully vested.
On May 9, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a grant of shares of restricted stock to independent board member Dayton Judd. The shares vest % on each of January 1, 2024 and January 1, 2025. As of the grant date, the fair value of the shares was $ thousand, to be amortized on a straight-line basis through December 31, 2024. As of September 29, 2024, there were unvested restricted shares outstanding.
On October 2, 2023, performance shares vested for reaching the 30-day VWAP for Tranche 1. The Company issued a total of shares on October 24, 2023 in settlement of the vested shares, net of tax withheld of $ thousand.
On December 22, 2023 and December 29, 2023, performance shares vested each date for reaching the 30-day VWAP for Tranche 2 and Tranche 3. On January 8, 2024 the Company issued a total of shares in settlement of the vested shares, net of tax withheld of $ thousand.
| 53 |
On March 11, 2024, performance shares vested each date for reaching the 30-day VWAP for Tranche 4. The Company issued a total of shares on March 13, 2024 in settlement of the vested shares, net of tax withheld of $ thousand.
On
May 1, 2024, the Company granted an aggregate of restricted stock units to eleven employees under
its 2023 Equity Incentive Plan. As of the grant date, assuming a
On May 1, 2024, there were shares vested under its 2023 Equity Incentive Plan for restricted stock units granted on May 1, 2023. On May 3, 2024, shares were issued to ten employees, net of tax withheld of $ thousand.
On May 17, 2024, performance shares vested for reaching the 30-day VWAP for Tranche 5. The Company issued a total of shares on May 17, 2024 in settlement of the vested shares, net of tax withheld of $ thousand.
On August 14, 2024, there were shares vested under its 2023 Equity Incentive Plan for restricted stock units granted on August 14, 2023. On August 20, 2024, shares were issued to one employee, net of tax withheld of $ thousand.
As of September 29, 2024, there were performance shares remaining to vest.
| Assumptions | ||||
| Performance Period Start | ||||
| Performance Period End | ||||
| Term of simulation (1) | years | |||
| Time steps in simulation | ||||
| Time steps per year | ||||
| Common share price at valuation date (2) | $ | |||
| Volatility (annual) (4) | % | |||
| Risk-free rate (annual) (5) | % | |||
| Cost of equity (6) | % | |||
| Dividend yield (3) | % | |||
| Tranche 1 | Tranche 2 | Tranche 3 | Tranche 4 | Tranche 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of performance shares in the Tranche (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value of One Performance share (7) | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||
| Total Fair Value of Tranche | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||
| Derived Service Period (Years) (7) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | ||
| (2) | ||
| (3) | ||
| (4) | ||
| (5) | ||
| (6) | ||
| (7) |
| 54 |
Stock Based Compensation Expense
Equity compensation is amortized based on a straight-line basis across the vesting or service period as applicable. The recorded compensation costs for restricted shares granted and restricted stock units and performance shares awarded as well as the unrecognized compensation costs are summarized in the table below:
| Recognized Compensation Expense | Unrecognized Compensation Expense | |||||||||||||||
| Year Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||||||
| September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | September 29, 2024 | October 1, 2023 | |||||||||||||
| Restricted Shares | $ | | $ | $ | | $ | ||||||||||
| Performance Shares | ||||||||||||||||
| Restricted Stock Units | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Stock Compensation | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
The unrecognized compensation expense for restricted shares and restricted stock units as of September 29, 2024, is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of years and years, respectively.
Note 11 — Defined Contribution Plan
The
Company sponsors a defined contribution pension plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code for all employees. Company contributions
are voluntary and are determined annually at the discretion of the Board of Directors at the beginning of each fiscal year. For the fiscal
years ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023,
Note 12 — Stockholders’ Equity
Dividends
There
were
Common stock
During
the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, there were common shares issued to officers and employees, net of tax withholding
of $
During
the twelve months ended October 1, 2023, there were common shares issued to officers, net of tax withholding of $
During the twelve months ended October 1, 2023, there were unvested restricted shares cancelled on the departure of a board member and unvested restricted shares granted to a newly elected board member.
On
September 22, 2021 the Company announced authorization for a $
During the twelve months ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, there were common shares repurchased through the program.
As of September 29, 2024, and October 1, 2023, the total outstanding common shares were and , respectively.
| 55 |
Note 13 — Income Taxes
The income tax provision for the years ended September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023 include the following:
| (Thousands) | ||||||||
| 2024 | 2023 | |||||||
| Current income tax expense: | ||||||||
| Current year federal income tax | $ | $ | ||||||
| Prior year tax adjustment | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Deferred income tax provision (benefit): | ||||||||
| Federal | ( | ) | ||||||
| Provision for income taxes, net | $ | $ | ||||||
As
of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023, Optex Systems Inc. has a net carrying value of $
The income tax provision for Optex Systems as of September 29, 2024 and October 1, 2023 differs from those computed using the statutory federal tax rate in the respective years due to the following permanent differences:
| 2024 | % | 2023 | % | |||||||||||||
| Tax provision at statutory federal rate | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
| Nondeductible expenses | ||||||||||||||||
| Other temporary adjustments | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Prior year federal income tax adjustment | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||
| Change in deferred tax valuation allowance | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||
| Provision for income taxes, net | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
Deferred income taxes recorded in the balance sheets result from differences between financial statement and tax reporting of income and deductions. A summary of the composition of the deferred income tax assets (liabilities) follows:
| (Thousands) | ||||||||
| Deferred Tax Asset | ||||||||
As of September 29, 2024 | As of October 1, 2023 | |||||||
| Stock Compensation | $ | $ | ||||||
| Inventory Reserve | ||||||||
| Unicap | ||||||||
| Deferred Compensation | ||||||||
| Property and Equipment | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Intangible Asset Amortization | ||||||||
| Contract Loss Reserve | ||||||||
| Accrued Paid Time Off | ||||||||
| Net Operating Losses | ||||||||
| Other | ||||||||
| Subtotal | $ | $ | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net deferred asset | $ | $ | ||||||
The
Company has a net loss carryforward of $
| 56 |
The Company applied FASB ASC 740-10 and has no unrecognized tax benefits. By statute, the tax years ended September 29, 2024, October 1, 2023 and October 2, 2022 are open to examination by the major taxing jurisdictions to which the Company is subject.
During
the twelve months ended September 29, 2024, the Company paid $
Note 14 — Subsequent Events
On
October 23, 2024 and December 10, 2024, the Company paid $
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As of September 29, 2024, management performed, with the participation of our Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer, an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Exchange Act. Our disclosure controls and procedures are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the report we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management including our Principal Executive Officer and our Principal Financial Officer, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures. Based on the evaluation, our Principal Executive Officer and our Principal Financial Officer concluded that, as of September 29, 2024, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
During the quarter ended September 29, 2024, there were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projection of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods is subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management has conducted, with the participation of our Principal Executive Officer and our Principal Financial Officer, an assessment, including testing of the effectiveness, of our internal control over financial reporting as of September 29, 2024. Management’s assessment of internal control over financial reporting was conducted using the criteria in the 2013 Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. In connection with our management’s assessment of our internal control over financial reporting as required under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, we have not identified any material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting as of September 29, 2024. We have thus concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of September 29, 2024.
Item 9B. Other Information
On
| 57 |
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this Item 10 will be included in the Proxy Statement or in an amendment to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item 11 will be included in the Proxy Statement or in an amendment to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this Item 12 will be included in the Proxy Statement or in an amendment to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item 13 will be included in the Proxy Statement or in an amendment to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this Item 14 will be included in the Proxy Statement or in an amendment to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 15. Exhibits
| (a)(1) | Financial Statements. The following financial statements of Optex Systems Holdings, Inc. are included in Part II, Item 8: |
| (a)(2) | Financial Statement Schedules. |
| All schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, or not required, or because the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto. |
| (a)(3) | Exhibits. |
| See Exhibit Index |
| 58 |
Exhibits
| 59 |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended October 3, 2021. |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K dated April 3, 2009. |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference from our Amendment No. 1 to Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on July 23, 2015. |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended October 3, 2021. |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference from our Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on May 19, 2009. |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K dated April 3, 2009. |
| (7) | Incorporated by reference from our Amendment No. 4 to Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on June 14, 2010. |
| (8) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on January 5, 2024. |
| (9) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on November 23, 2016. |
| (10) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on November 23, 2016. |
| (11) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on July 10, 2017. |
| (12) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, dated November 21, 2022. |
| (13) | Incorporated by reference from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended October 3, 2021. |
| (14) | Incorporated by reference from Annex B to our Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A, filed on January 17, 2023. |
| (15) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K, dated March 22, 2023. |
| (16) | Incorporated by reference from our Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on May 19, 2009. |
| (17) | Incorporated by reference from our Current Report on Form 8-K dated April 3, 2009. |
| (18) | Incorporated by reference from our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2024. |
| (19) | Incorporated by reference from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended October 1, 2023. |
† Management contracts and compensatory plans and arrangements.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
| 60 |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| OPTEX SYSTEMS HOLDINGS, INC. | ||
| By: | /s/ Danny Schoening | |
| Danny Schoening, Principal Executive Officer and Director | ||
| Date: December 19, 2024 | ||
| By: | /s/ Karen Hawkins | |
| Karen Hawkins, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer | ||
| Date: December 19, 2024 | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Danny Schoening | ||||
| Danny Schoening | Chairman, Principal Executive Officer and Director | December 19, 2024 | ||
| /s/ Karen Hawkins | ||||
| Karen Hawkins | Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer | December 19, 2024 | ||
| /s/ Rimmy Malhotra | ||||
| Rimmy Malhotra | Director | December 19, 2024 | ||
| /s/ Dale Lehmann | ||||
| Dale Lehmann | Director | December 19, 2024 | ||
| /s/ Dayton Judd | ||||
| Dayton Judd | Director | December 19, 2024 |
| 61 |